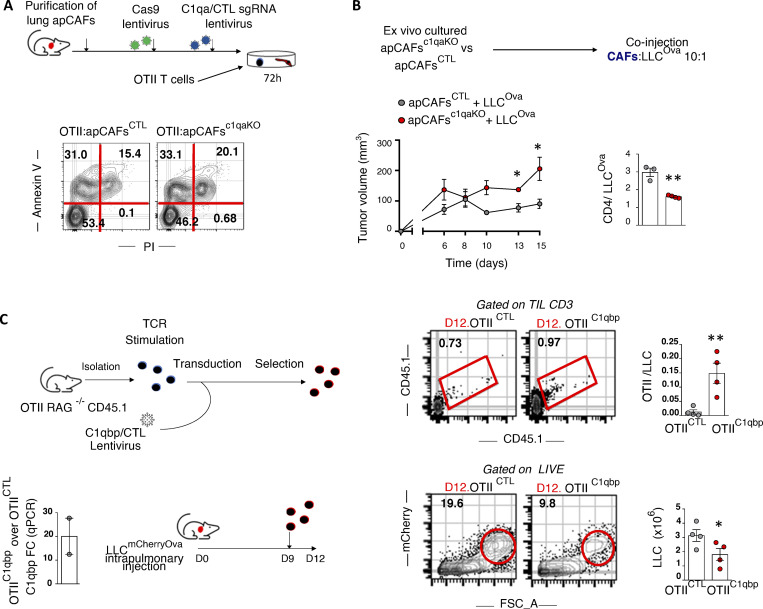
Figure 7.
In vivo MHCII tumor immunity depends on apCAF C1q, CD4 T cell C1qbp. (A) C1q was knocked out of primary lung apCAFs via CRISPR-Cas9. MHCII+CAFc1qa KO versus control (CTL) MHCII+CAFs were co-cultured with OTII T cells. Apoptosis was measured by Annexin V/dead staining. Representative FACS plots of two experiments. (B) MHCII+CAFc1qa KO versus control MHCII+CAFs were cotransplanted with LLCmcherryOva cells in syngeneic mice. Tumor growth was measured. Cumulative data of CD4 T cell numbers normalized to cancer cell numbers. Absolute numbers were assessed by FACS with counting beads. (n = 3 or 4 mice per group, pooled from two experiments). (C) C1qbp overexpressing OTII T cells were adoptively transferred in LLCmcherryOva lung tumor–bearing mice. Representative FACS plots of LLCmcherryOva cells and OTII cells in digested lung tumors. Cumulative data (n = 4 per group, pooled from two experiments). (A–C) *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Error bars, mean ± SEM; two-tailed unpaired t test. FSC-A, forward scatter-A; sgRNA, single-guide RNA.