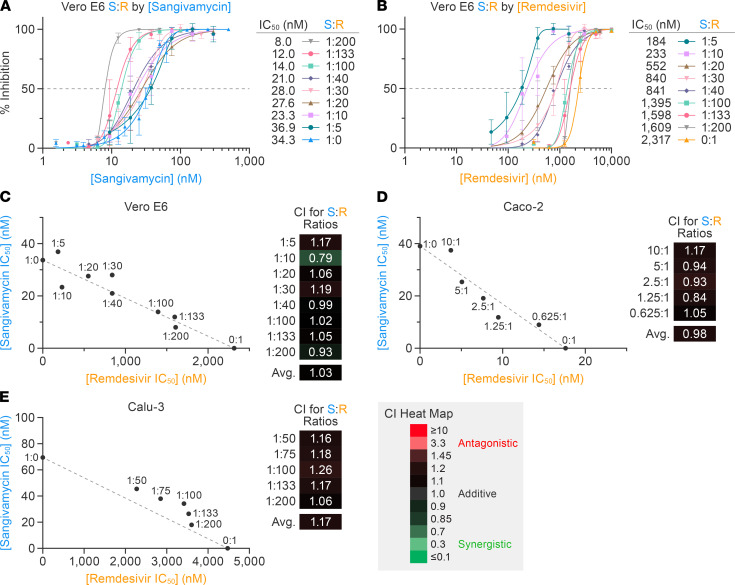
Figure 4. Combining sangivamycin and remdesivir results in an additive effect against SARS-CoV-2 in multiple cell types.
Constant ratios of sangivamycin to remdesivir (S:R) were used to evaluate combination effect against SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells and plotted relative to (A) sangivamycin concentration and (B) remdesivir concentration. Each dose combination was run in triplicate with error bars representing standard deviations (SDs). (C) Effects of different combinations of sangivamycin-to-remdesivir ratios on viral infection rate, fit to the Loewe interaction model. Isobologram showing ratio pairs that resulted in 50% virus inhibition calculated from the curves in A and B plotted on the y axis (values from A) and x axis (values from B) relative to the additive (dotted) line drawn between the IC50 values for sangivamycin (S:R = 1:0) and remdesivir (S:R = 0:1) alone. The results of experiments similar to those shown in A and B performed on Caco-2 and Calu-3 cells are shown in Supplemental Figure 3. (D and E) Isobolograms as in C calculated based on results in Supplemental Figure 3. The CI heatmap legend indicates color coding for S:R antagonism (red), additive efficacy (black), or synergy (green) based on ref. 23. CI, combination index.