Figure 8.
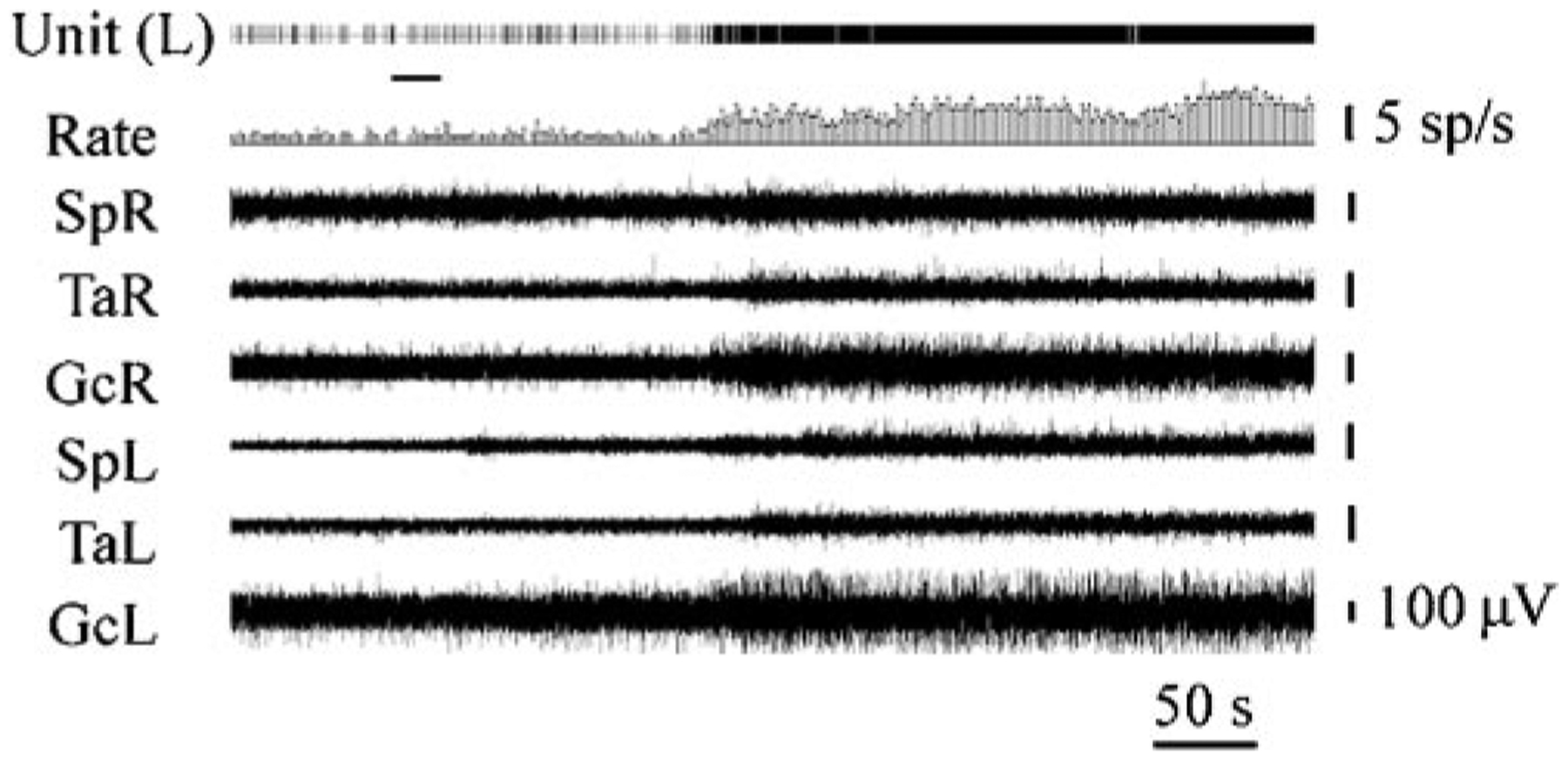
Effect of Hcrt microinjection adjacent to the locus coeruleus. This figure shows that Hcrt microinjection into the locus coeruleus raises muscle tone ipsilateral to the injection. The loss of this excitatory effect of Hcrt contributes to cataplexy, the sudden loss of muscle tone experienced by most narcoleptics. Locus coeruleus activity ceases during cataplexy (Wu et al. 1999). SpR, SpL: electromyogram (EMG) of muscle splenius (right and left side); TaR, TaL: EMG of tibialis anterior muscle (right and left side); GcR, GcL: EMG of gastrocnemius muscle (right and left side). (From Kiyashchenko et al. 2001)
