Fig. 7.
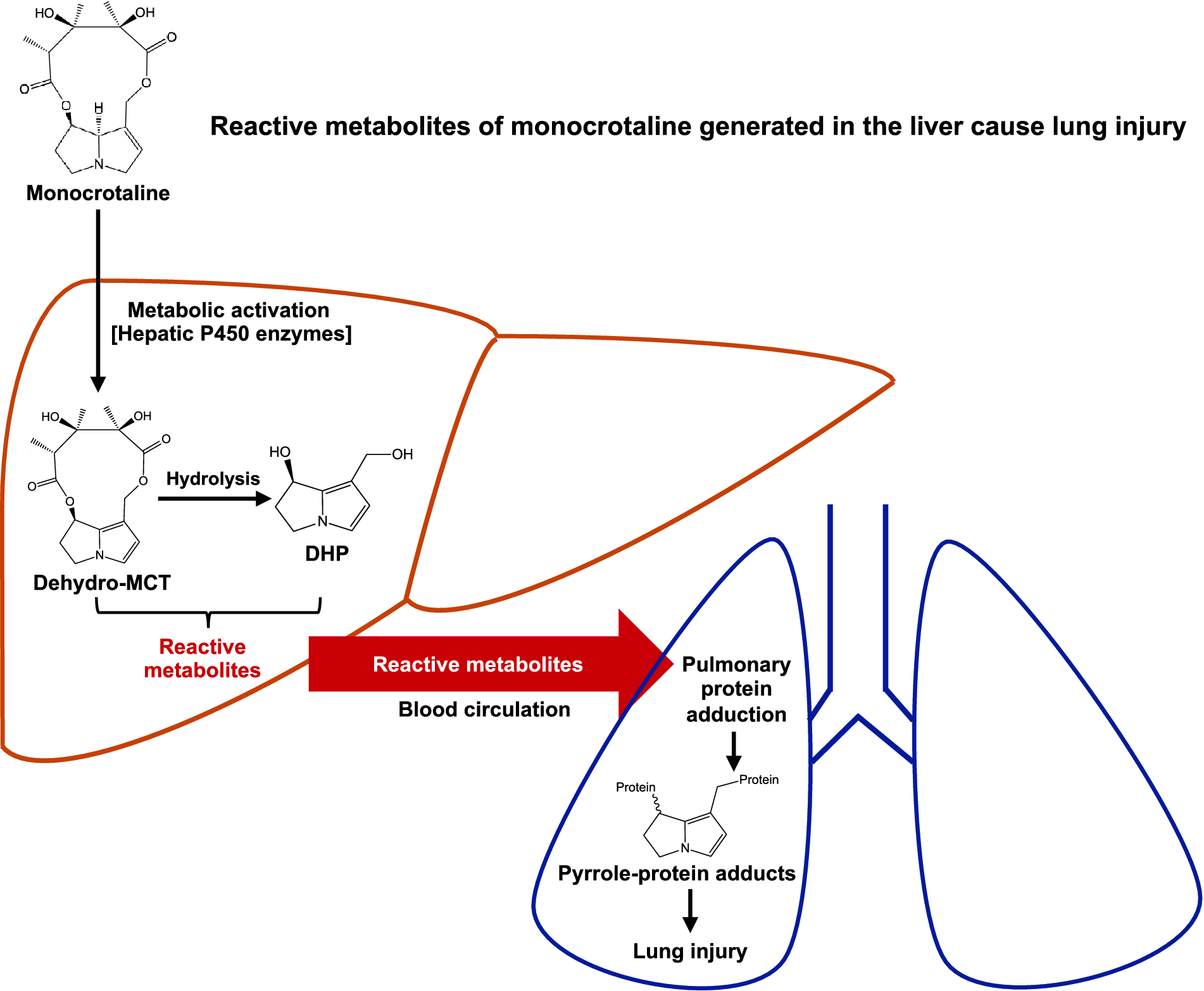
Schematic illustration of the initial biochemical mechanism of MCT-induced lung injury. The metabolic activation of the ingested MCT is mediated by hepatic P450 enzymes. The reactive metabolites of MCT generated in the liver are carried by blood efflux from the liver and transported into the lungs to form pulmonary pyrrole-protein adducts, thereby causing lung injury.
