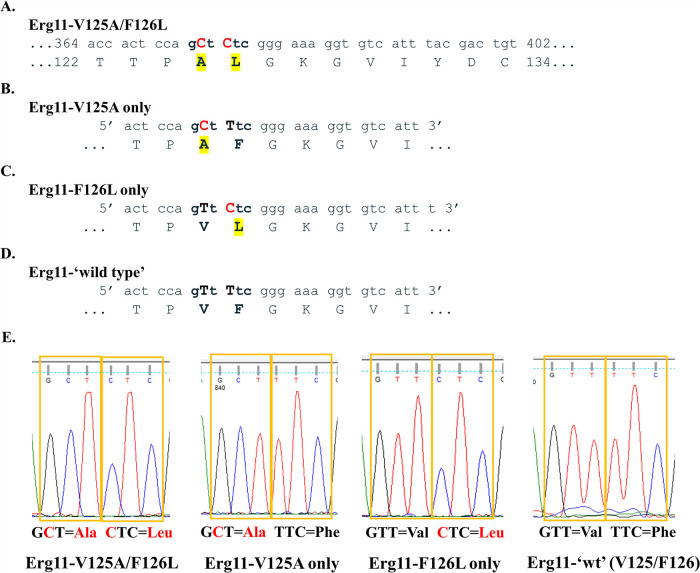
FIG 1.
Molecular dissection of C. auris Erg11 V125A and F126L amino acid substitutions. (A) Region of C. auris clade III ERG11 DNA that displays nucleotide mutations (T374C/T376C) in red and resulting protein alterations (V125A/F126L) in yellow highlight. (B) Forward mutagenic primer used to revert leucine (L) back to phenylalanine (F). After mutagenesis, this construct contained only V125A (pCauErg11-V125A). (C) Forward mutagenic primer used to revert alanine (A) back to wild-type valine (V). After mutagenesis, this construct contained only F126L (pCauErg11-F126L). (D) Forward mutagenic primer used to revert leucine (L) back to phenylalanine (F) using the pCauErg11-F126L plasmid as a template. After mutagenesis, this construct contained both wild-type nucleotides and amino acids (pCauErg11-‘wt’). (E) Plasmid sequencing chromatograms of relevant codons corresponding to the 125th and 126th amino acids following mutagenesis and propagation in Escherichia coli.