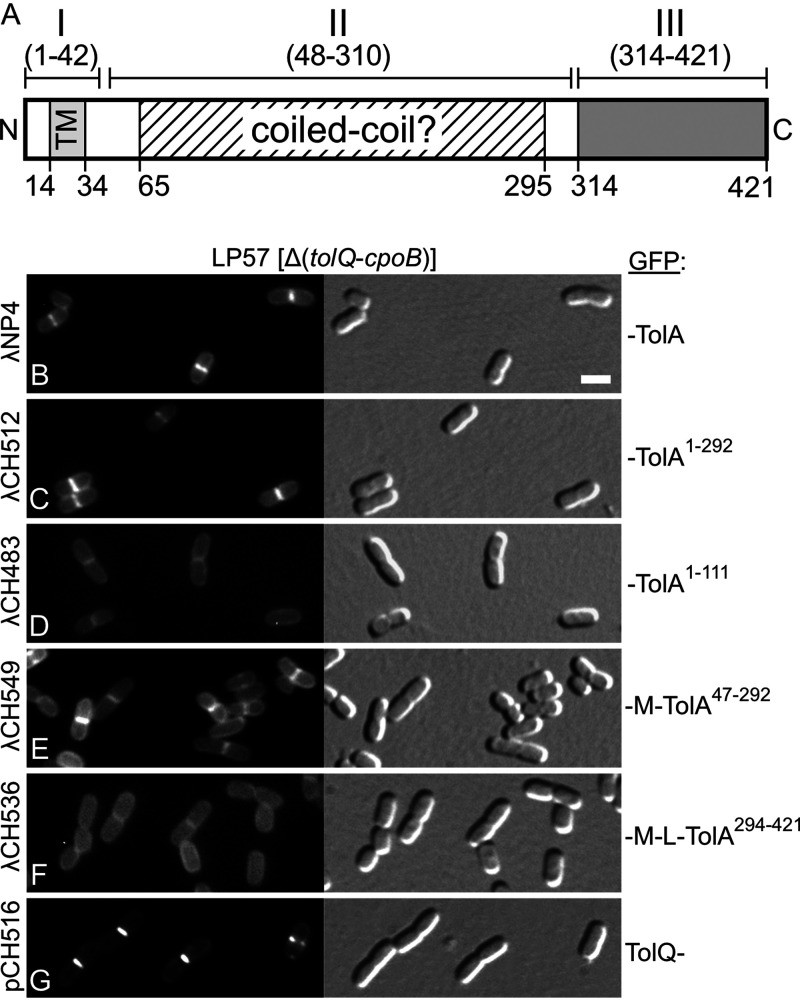
FIG 2.
Recruitment of TolA47-292 (∼TolAII) to division sites in the absence of other Tol-Pal components. (A) Schematic showing domain organization and other features of the E. coli TolA protein. Domain TolAII (TolA48-310) is linked to domains TolAI (TolA1-42) and TolAIII (TolA314-421) by stretches of five and three glycine residues, respectively. TolAI includes the cytoplasmic N-terminal peptide (TolA1-13), the transmembrane helix (TM, TolA14-34), and some periplasmic residues (TolA35-42). TolAII is dominated by a long stretch of residues (TolA65-295) with a high propensity to adopt the α-helical coiled-coil fold as predicted with Paircoil2 (P score cutoff = 0.03) (118). TolAIII (TolA314-421) is a well-defined C-terminal periplasmic domain of known structure (53–55). (B to G) Fluorescence (left) and DIC (right) images of live LP57 (Δ[tolQ-cpoB]) cells producing GFP fusions to full-length TolA1-421 (TolAI+II+III) (B), TolA1-292 (∼TolAI+II) (C), TolA1-111 (∼TolAI) (D), MalF2-39-TolA47-292 (∼TolAII) (E), MalF2-39-RodZ139-255-TolA294-421 (∼TolAIII) (F), or full-length TolQ (G). MalF2-39 (M) includes the first transmembrane helix (MalF19-35) of the MalF protein (89), and RodZ139-255 (L) corresponds to the periplasmic linker that connects the TM and C-terminal domains of the RodZ protein (90). Fusions were encoded on lysogenic phages λNP4 (Plac::gfp-tolA) (B), λCH512 (Plac::gfp-tolA1-292) (C), λCH483 (Plac::gfp-tolA1-111) (D), λCH549 (Plac::gfp-malF2-39-tolA47-292) (E), or λCH536 (Plac::gfp-malF2-39-rodZ139-255-tolA294-421) (F) or on plasmid pCH516 (Plac::tolQ-gfp) (G). Cells were grown for ∼3.5 mass doublings to OD600 = 0.5 to 0.6 in M9-maltose medium with 37 μM (B to F) or 5 μM (G) IPTG. Bar equals 2 μm.