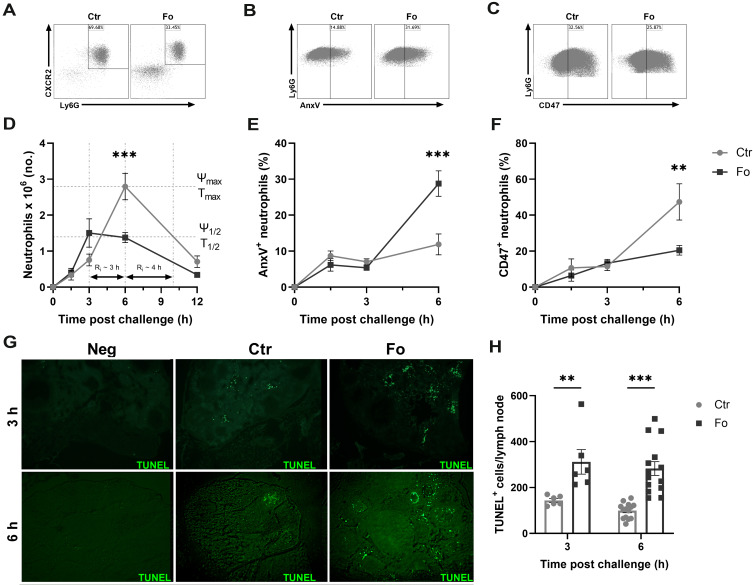
Figure 4.
Dietary fish oil shortens the resolution interval, enhances neutrophil apoptosis and egress to draining lymph nodes but decreases neutrophil CD47 expression. Mice were fed control (Ctr, grey lines with grey circles) or fish oil (Fo, black lines with black squares) diets for 5 weeks. They were immunized twice with mBSA with a 2-week interval and challenged intraperitoneally. Mice were sacrificed at 0, 1.5, 3, 6, and 12 h post-challenge and peritoneal cells and mesenteric lymph nodes harvested. Peritoneal cells were stained with monoclonal antibodies against CXCR2, Ly6G, and CD47. Apoptotic neutrophils were stained with FITC-labeled annexin V (AnxV). Neutrophils were defined as CXCR2+Ly6G+ granulocytes. Representative dot plots of neutrophil gating strategy (A), AnxV+ neutrophils (B) and CD47+ neutrophils (C) 6 h after inflammation induction in mice fed either Ctr or Fo diets. Neutrophil numbers with time after inflammation induction in mice fed Ctr and Fo diets determining the infiltration peak (Ψmax), peak infiltration time (Tmax), half the peak neutrophil number (Ψ1/2) and the time when neutrophil numbers reach half Ψmax (T1/2) to determine the resolution interval (Ri), n = 6–12 for 0, 3 and 12 h and 47–50 for the 6 h time-point (D). Percent neutrophils stained with AnxV (E) or CD47 (F) 6 h after inflammation induction in mice fed Ctr and Fo diets, n = 6 for all time-points. Representative TUNEL staining of mesenteric lymph nodes from mice fed Ctr or Fo diets at 3 and 6 h following inflammation induction (G). TUNEL+ cells in all stained lymph nodes from mice fed Ctr and Fo diets, n = 6 for the 3 h time-point and 14 for 6 h post-challenge (H). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n = 6–40. Results are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean from data collected from at least two independent experiments.