Figure 2. Distinct transcriptional programs associated with diet and exercise in the aging hippocampus.
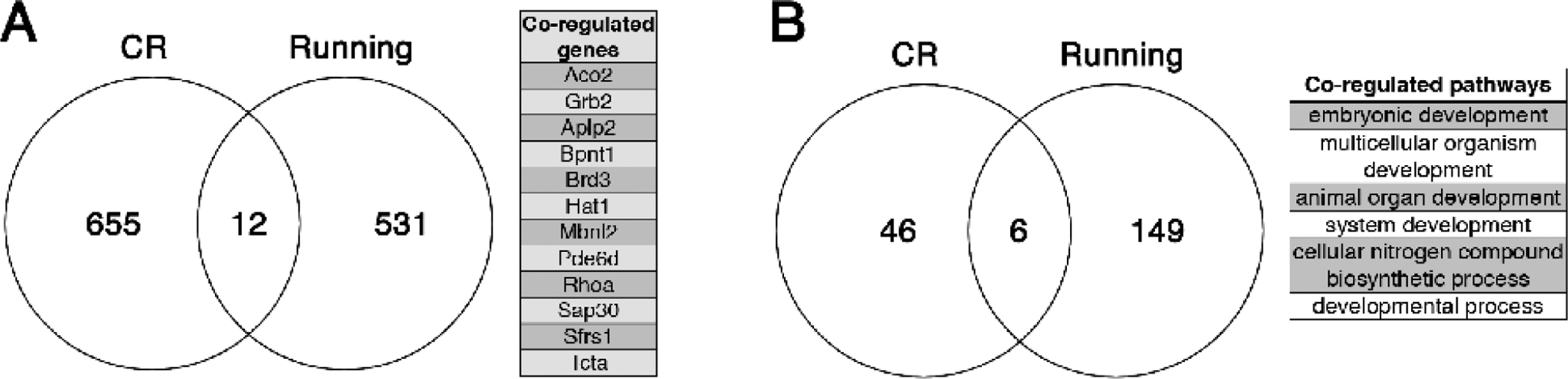
Mining the data from Mattson lab publications investigating the impact of lifelong caloric restriction (CR) or wheel running uncovered potential evidence of distinct transcriptional programs for energy restriction and expenditure in the aged hippocampus (Xu et al, 2007; Stranahan et al, 2010). Comparing hippocampal gene expression profiles following lifelong caloric restriction in 16-month-old mice (Xu et al, 2007) with those observed after lifelong wheel running in 18–20-month-old mice (Stranahan et al, 2010) revealed limited overlap at the level of individual genes (A) and Biological Processes associated with the corresponding Gene Ontology terms (B). Mark Mattson’s unique approach incorporated both breadth and depth to uncover these and other insights into metabolic regulation of brain aging.
