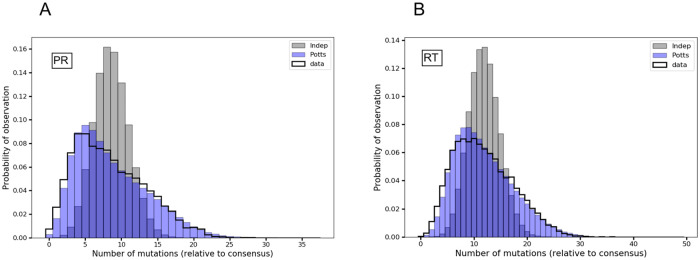
Fig 2. Distribution of the number of mutations (hamming distances) in drug-experienced HIV-1 sequences as captured by the Potts and independent models.
Probabilities of observing sequences with any k number of mutations relative to the HIV-1 subtype B wild-type consensus sequence as observed in original MSA (black) and predicted by the Potts (blue) and independent (gray) models are shown for HIV-1 protease (PR) in (A), and reverse transcriptase (RT) in (B), respectively. The independent model predicted distribution does not accurately capture the distribution of hamming distances in the dataset MSA, especially near the ends of the distribution with either very low or very high number of mutations, where the epistatic effects can be more significant.