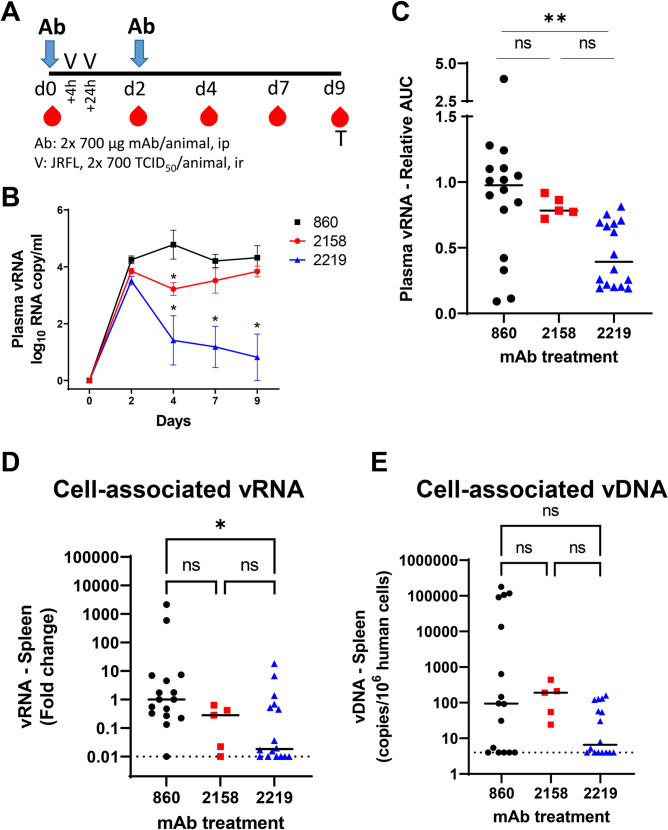
Fig 1. The capacity of V2i mAb 2158 and V3 mAb 2219 to reduce virus infection in CD34+ HSC-engrafted humanized mice upon rectal challenge with HIV-1 JRFL IMC.
A) Schematic of experimental protocol showing that mice received intraperitoneal administration of mAb at day 0 and were challenged rectally with HIV at 4 hours and 24 hours. Animals received the second dose of mAb at day 2. Virus dose (2x700 TCID50 per animal) was pre-determined to yield infection in all control mice. Blood and tissue samples were collected at the designated days for measurement of vRNA and vDNA in individual animals. B) Mean plasma vRNA loads from day 0 to day 9 in each group of animals that received control mAb 860, V2i mAb 2158, or V3 mAb 2219. Data from one of three experiments are shown. C) Plasma vRNA loads of individual mice in each of the three groups. Area under the curve (AUC) of vRNA over time was calculated. Data are presented as relative AUC over mean AUC of the control 860 group included in each experiment. Three experiments were performed with cohorts of mice engrafted with different HSC donors. N = 16, 5, and 16 for mice treated with 860, 2158, and 2219, respectively. D) Relative levels of cell-associated vRNA detected in the spleen collected at the end of experiment from individual mice in the three groups. Data from three experiments are compiled and presented as fold changes over median vRNA of the control 860 group in each experiment. E) Cell-associated vDNA levels in the spleen of mice from the three groups. Data are shown as vDNA copies per 106 human CD45+ cells. Statistical analysis was done with Kruskal Wallis one-way ANOVA test with Dunn’s multiple comparison. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ns, not significant (p >0.05). Horizontal bars: median. Dotted lines: detection limit.