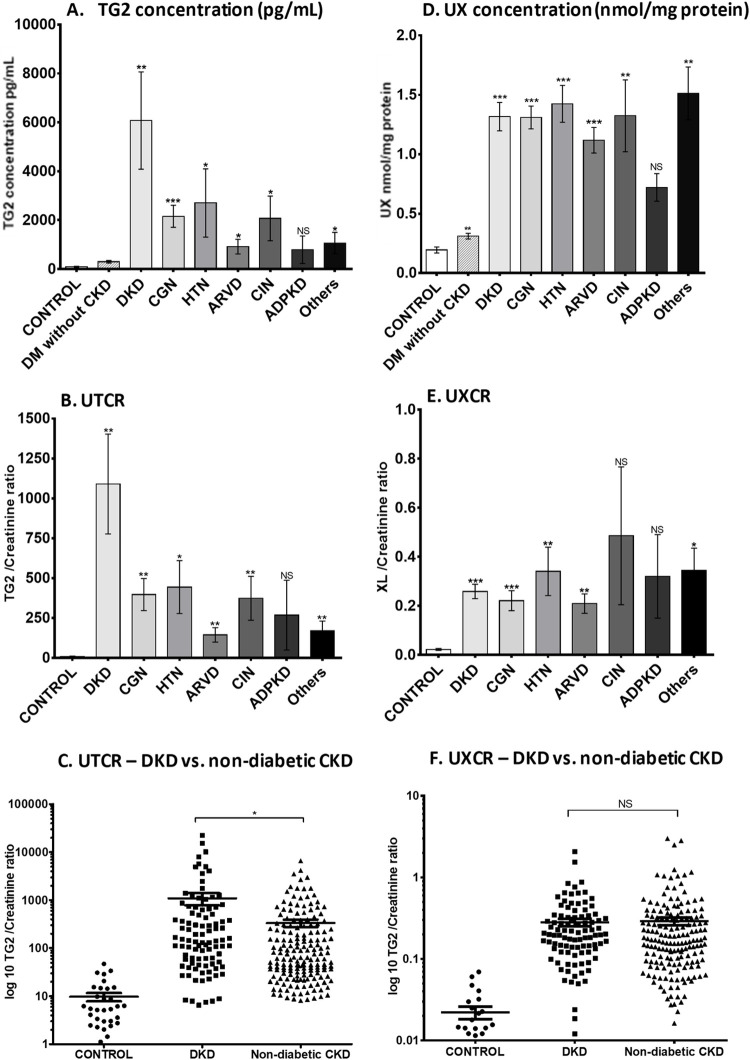
Fig 2. Urinary TG2 and ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine excretion in patients with different causes of CKD.
Urinary TG2 was measured by an in-house ELISA in patients with CKD (total n = 290), healthy volunteers (n = 33) and expressed as a concentration (ng/mL) (A), then corrected to a creatinine ratio (D) with variation displayed as a scatter plot of UTCR in DKD (n = 90) and non-diabetic CKD patients (n = 200), with y axis in log 10 scale (B). ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine crosslink (Glu-Lys) was measured in protein precipitates from human urine samples by cation exchange chromatography and displayed as mean Glu-Lys per mg urine protein ± SD calculated by AUC of peaks (E) and then corrected to a creatinine ratio (C) using a log 10 scale. Variation is shown using a scatter plot of UXCR in DKD and non-DKD CKD. Results are displayed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance is shown by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 between CKD patients and HV. ADPKD = autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; ARVD = atherosclerotic renovascular disease; AUC = area under the curve; CGN = chronic glomerulonephritis; CIN = chronic interstitial nephritis; CKD = chronic kidney disease; DKD = diabetic kidney disease; DM = diabetes mellitus; ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HTN = hypertensive nephrosclerosis; HV = healthy volunteer; NS = not statistically significant; SD = standard deviation; TG2 = transglutaminase 2; UTCR = urinary TG2:creatinine ratio; UX = urinary ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine; UXCR = urinary ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine:creatinine ratio.