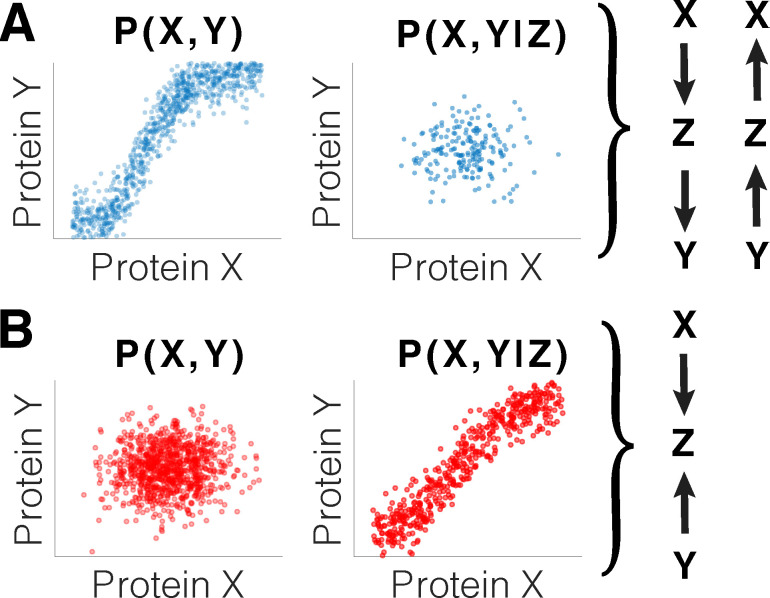
Fig 1. Inference of direct regulatory interactions with minimal assumptions.
(A) The observed joint distributions of proteins X and Y across many single cells are consistent with 2 models in which protein Z is a confounder. (B) The joint distributions of proteins X and Y across many single cells are consistent with a “collider” model, in which X and Y collide at Z, inducing dependence conditional on Z. The arrows indicate directions of causality (positive or negative regulation), and in the collider model one of the arrows corresponds to positive and the other to a negative regulatory effect. Such inference of direct regulatory interactions requires no specific assumptions, but it does require accurate measurements across many single cells.