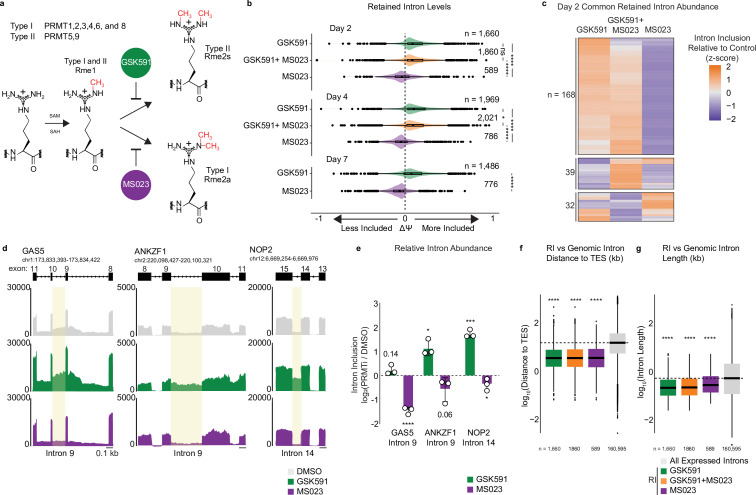
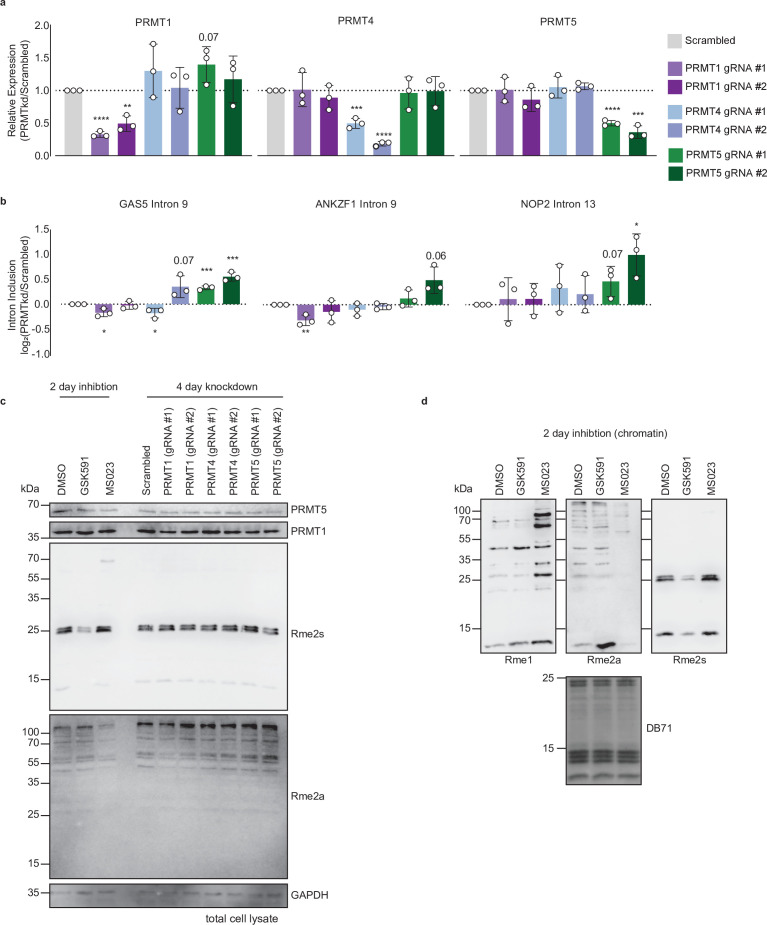
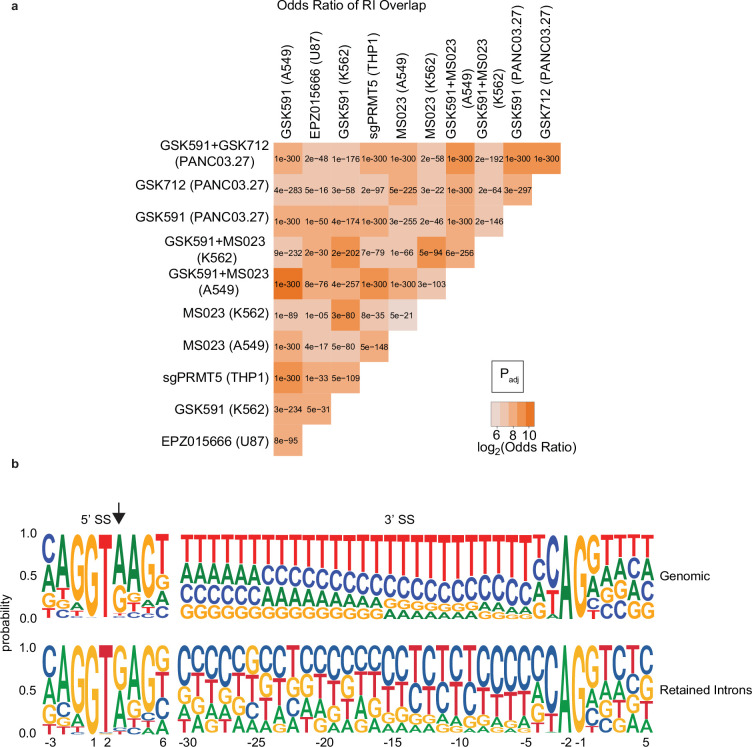
Figure 1. Type I PRMTs and PRMT5 inversely regulate intron retention.
(a) Overview of protein arginine methyltransferases and their catalyzed reactions. (b) Comparison of ΔΨ for retained introns (RI) following PRMT inhibition where ΔΨ=Ψ (PRMT inhibitor)–Ψ (DMSO). Significance determined using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; *<0.05, ****<0.0001, ns=not significant. (c) Comparison of ΔΨ z-score for common RI after 2-day treatment with PRMT inhibitors. (d) Genome browser track of poly(A)-RNA seq aligned reads for GAS5, ANKZF1, and NOP2. Yellow shading denotes RI. Scale (0.1 kb) indicated in lower right corner. (e) RT-qPCR of RI highlighted in panel (d). Data are represented as mean ± SD. (f, g) Comparison of RI and A549-expressed intron distance to the transcription-end site (TES) (f) or intron length (g) in log10(kb). Dashed line indicates genomic median; solid line within boxplot is condition-specific median. Significance determined using Wilcoxon rank-sum test; ****<0.0001.