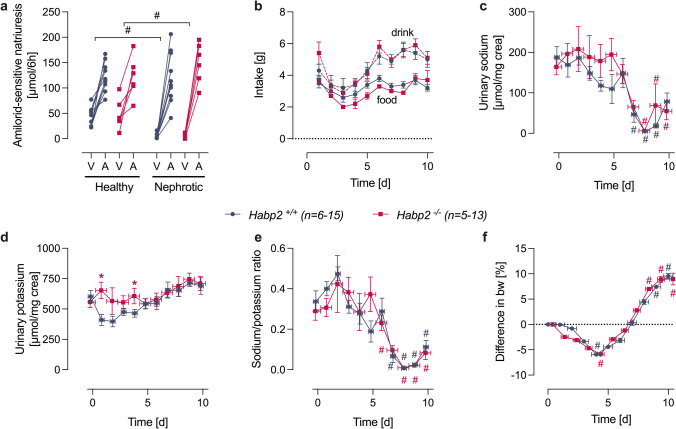
Fig. 4.
Impact of FSAP deficiency on ENaC activation and sodium retention in experimental nephrotic syndrome. a Natriuretic response to vehicle (injectable water, 5 µl g−1 bw) or amiloride (10 µg g−1 bw i.p.) in healthy and nephrotic Habp2+/+ and Habp2−/− mice. Urine was collected for 6 h after injection and all mice underwent vehicle and amiloride injection sequentially (at day − 14/ − 13 and day 7/8, respectively). b–f Course of food and fluid intake, urinary sodium and potassium excretion and its ratio in spot urine samples and body weight taken in the morning after induction of nephrotic syndrome in Habp2+/+ and Habp2−/− mice. Note: Due to a variance of one day in the onset of proteolytic ENaC activation in experimental nephrotic syndrome, the data in c–e were fit to the day of lowest urinary sodium (day 8) and to the day of lowest bodyweight (day 4) (f), which results in an x error depicted in the corresponding graphs. #Significant difference between healthy and nephrotic state. *Significant difference between the genotypes