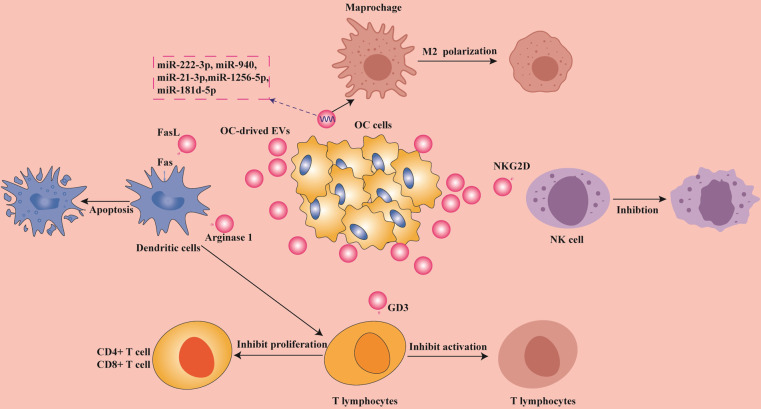
Fig. 3. The role of EVs in OC immune evasion.
OC-derived EVs inhibit the activation of DC cells, induce the polarization of macrophages, inhibit the cytotoxicity of NK cells, and regulate the function of T cells. The miRNAs carried in EVs secreted by OC cells promote the conversion of macrophages into M2 phenotype [124], and the FasL carried on the surface induces the apoptosis of DCs [128]. EV cargo also inhibits the proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells through the presentation of DCs [145]. EV cargo directly stimulates T cells and NK cells as well as inhibits their functional activation [136, 144]. EVs help OC cells produce immune evasion through these mechanisms of action.