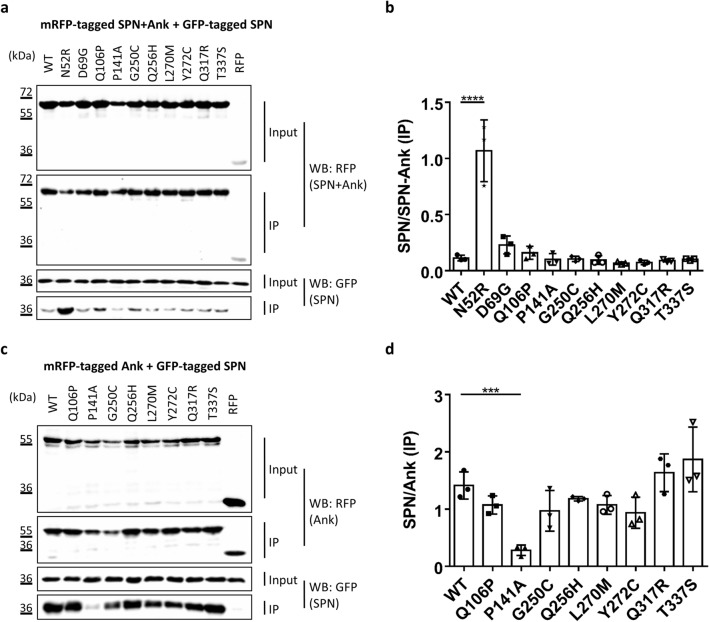
Figure 5.
(a) RFP-tagged WT and mutant variants of the Shank3 N-terminus (SPN + Ank domains), or mRFP alone, were coexpressed in 293 T cells with the GFP-tagged SPN domain of Shank3. The N52R mutant, which was designed based on the 3D structure of Shank3 to disrupt the SPN − Ank contact, was included as a positive control here. After cell lysis, RFP-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated using the mRFP-trap matrix. Input and precipitate samples were analysed by Western blotting using mRFP- (upper panels) and GFP-specific antibodies (lower panels). (b) Quantitative analysis. Signal intensities in IP samples for GFP-SPN were divided by IP signals for mRFP-Shank3 variants. ****Significantly different from WT, p < 0.0001; ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (c) The experiment was repeated as in a, however using a Shank3 construct coding for Ank repeats only. d. Quantitative analysis performed as in (b). ***Significantly different from WT, p < 0.001; data from three independent experiments; ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.