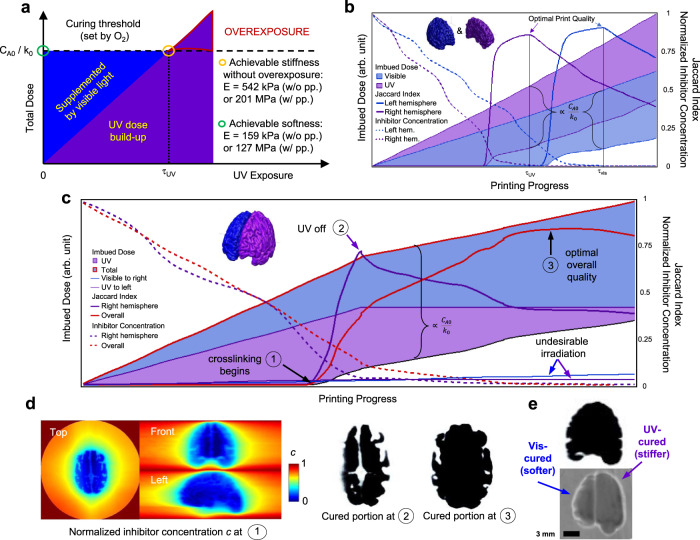
Fig. 3. The achievable stiffness contrast in DCTVP is limited by the curing threshold of free radical polymerization set by the initial inhibitor concentration.
a Both light sources contribute to free radical polymerization. The dual-color design of a multimaterial object starts with the design of the anticipated UV dose distribution (purple shaded), which spatially defines the relative stiffness inside the workpiece. The visible light dose build-up is then calculated to supplement doses to voxels that would not receive sufficient UV irradiation to initiate the crosslinking (blue shaded). The softest workpiece (green circle) would be produced when the curing dose is supplied only by the visible light source. Similarly, the hardest workpiece (yellow circle) would be produced if it received only UV irradiation. τUV is the exposure time when an object was cured using UV alone. Beyond τUV, the object keeps hardening, but its geometric fidelity decreases because the voxels in its vicinity polymerize undesirably. b Evolution of imbued doses, printing quality (measured using the Jaccard index), and normalized inhibitor concentration in the targeted subvolume if the two hemispheres of the brain model were printed individually using single-color TVP. Only doses contributed to inhibitor consumption are shaded. The blank space below the shaded areas indicates the doses absorbed by cured resin. c Evolution of imbued doses, printing quality, and normalized inhibitor concentration when the two hemispheres were printed simultaneously using DCTVP. The two thin solid lines show the UV irradiation received by the left hemisphere (purple) and the visible light irradiation received by the right hemisphere (blue). d Distribution of inhibitor concentration (c) in the curing volume at time point ① (polymerization initiation) and the cured portions (top view) at time points ② (optimal UV exposure) and ③ (optimal overall quality). e The front view of the cured portion when the curing sequence in c was followed. Top: model simulation; bottom: surveillance snapshot.