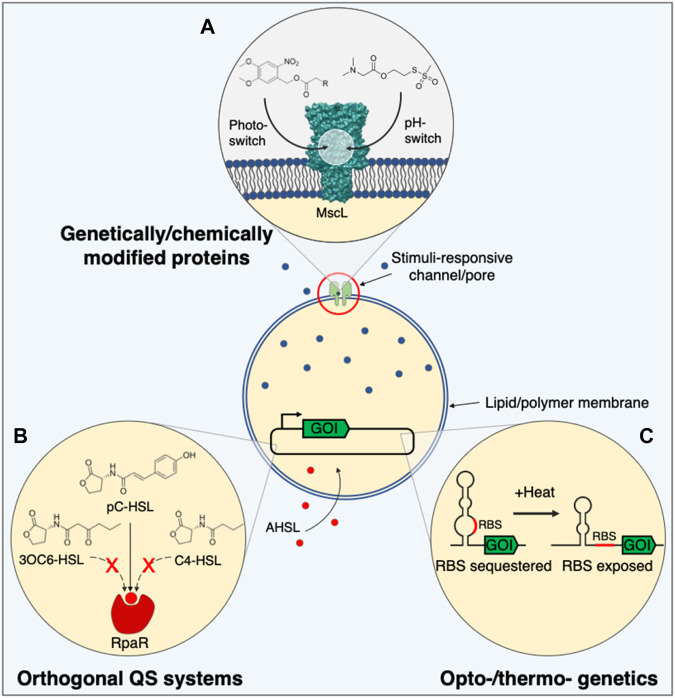
FIGURE 2.
Alternative tools for controlling synthetic cell communication. (A) Gateable pore or channel proteins engineered with stimuli-responsive moieties might be used to control the delivery or release of membrane-impermeable signalling molecules in a spatiotemporal or context-dependent manner. (B) Orthogonal quorum sensing systems that recognise different acyl-homoserine lactones, and with greater stringency, could diversify the molecules that synthetic cells utilise to regulate gene expression. (C) Regulating gene expression inside synthetic cells with temperature or light might offer greater user-defined control over synthetic cell communication for more widespread applications. 3OC6-HSL, N-3-oxo-hexanoyl homoserine lactone; AHSL, acyl-homoserine lactone; C4-HSL, N-butanoyl-l-homoserine lactone; GOI, gene of interest; MscL, mechanosensitive channel of large conductance; pC-HSL, para-coumaroyl-homoserine lactone; QS, quorum sensing; RBS, ribosome binding site; RpaR, pC-HSL transcription regulator.