Figure 2.
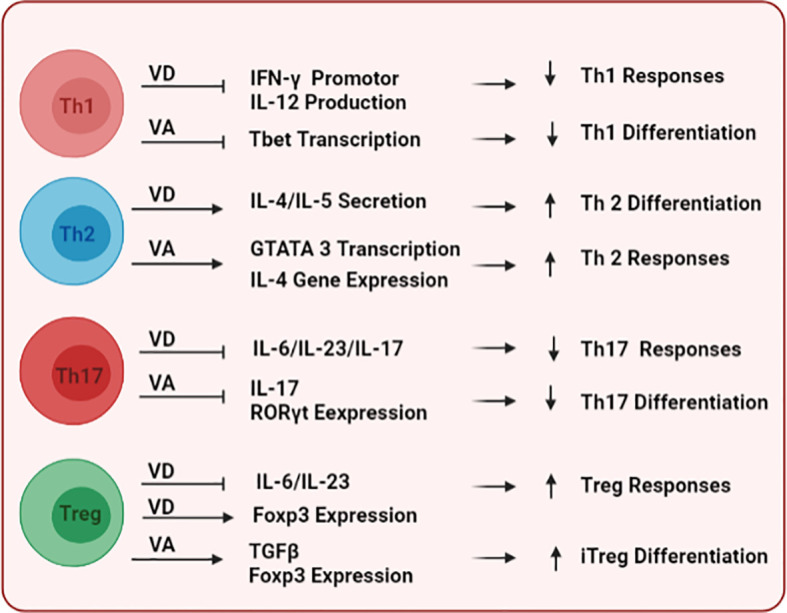
The immunomodulatory effects of vitamins D and A on T cells. Following their binding to DNA responsive elements of target genes, both vitamins differentially modulate key transcription factors and stimulatory cytokine signals to shape the commitment and functional responses of multiple T-cell subsets including Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg.
