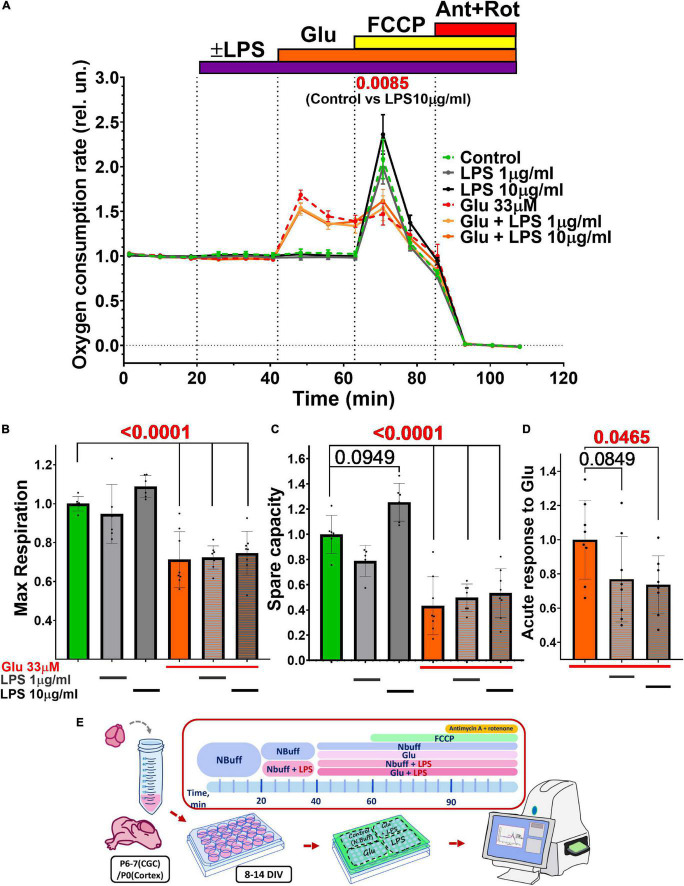
FIGURE 6.
Effect of glutamate (Glu) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) by cultured rat cerebral neurons. (A) The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) normalized to the culture density in each well of the plate, and then normalized to the basal OCR values (100–200 pmol O2/min) determined during the first 20 min of the experiment run. Agent concentrations were as follows (μM): Glu - 33, protonophore FCCP - 1, inhibitors of the respiratory chain antimycin A (Ant)-0.5, and rotenone (Rot)-0.5. Average values are given for 2 experiments (6 wells). The data are presented as Means ± SEM. Statistically significant differences were found using 2-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons (Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test), LPS 10 μg/ml compared to control. (B–D) Effect of LPS and Glu on (B) the maximum respiration rate, (C) the spare respiratory capacity, and (D) the acute response of OCR to glutamate (33 μM, first 5 min of action). The data are presented as Means ± SD (1-way ANOVA + Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). Calculation of maximal OCR, spare respiratory capacity, and acute response to Glu were performed according to Gerencser et al. (2009) (see the section “Materials and Methods”). Schematic of experimental design for panels A–D (E).