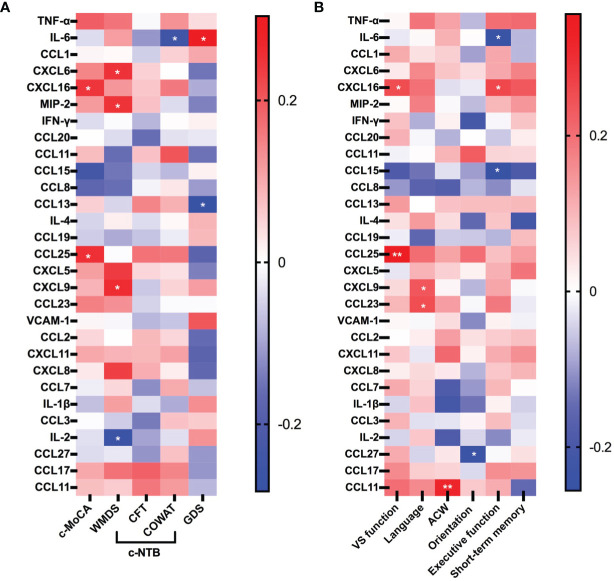
Figure 4.
Heatmap showing correlations between the concentrations of cytokines and chemokines with clinical characteristics of LLD and aMCI patients. (A) Association among proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and clinical scores reflecting the severity of cognition and depression. (B) Association among proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and subdomains of cognitive scores. The six neurocognitive domains shown in Figure 3B are the subdomains of the MoCA; red color indicates a positive correlation, and blue indicates a negative correlation; p-values are presented, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. C-MoCA, Chinese version of Montreal Cognitive Assessment; WMDS, Wechsler Memory digit span; CFT, Category Fluency Test; COWAT, Controlled Word Association Test; GDS, Geriatric Depression Scale; ACW, attention, concentration, and working memory; vs. function, visual–spatial function. Six CXC chemokine ligands (CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL8, CXCL9, CXCL11, and CXCL16) and 15 CC chemokine ligands (CCL1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL17, CCL19, CCL20, CCL23, CCL24, CCL25, and CCL27). MIP2, microphage inflammatory protein-2; IL-2ha, interleukin-2; IL-4, interleukin-4; IL-6, interleukin-6; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β, interleukin-1-beta; IFN-γ, interferon-γ-inducing factor.