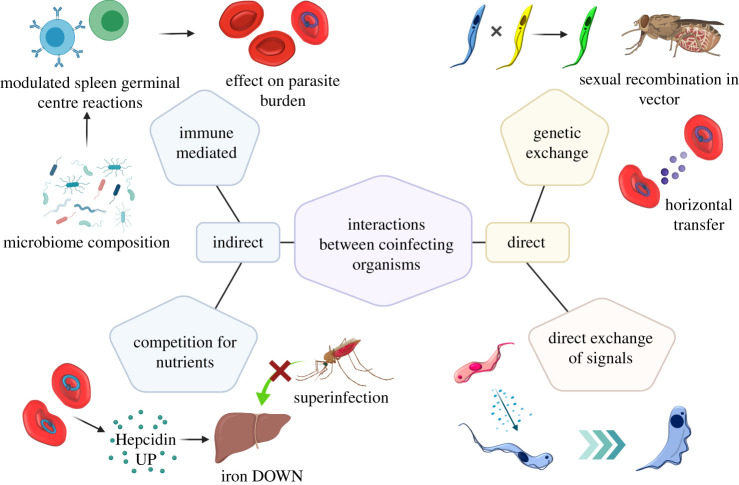
Figure 2.
Mechanisms that can mediate the interactions between co-infecting organisms. Examples of direct and indirect mechanisms of interaction are illustrated. Genetic exchange: sexual exchange between African trypanosomes in a co-infected tsetse fly, or horizontal transfer of DNA between Plasmodium infected red blood cells via extracellular vesicles. Direct exchange of signals: interspecies quorum sensing between African trypanosomes altering transmission potential. Competition for nutrients: an established Plasmodium infection increases host production of hepcidin diverting iron away from the liver, inhibiting invasion by superinfecting parasites. Immune mediated: the microbiota can influence the immune environment of a host to affect malaria infection. Created with BioRender.com. (Online version in colour.)