Figure 5.
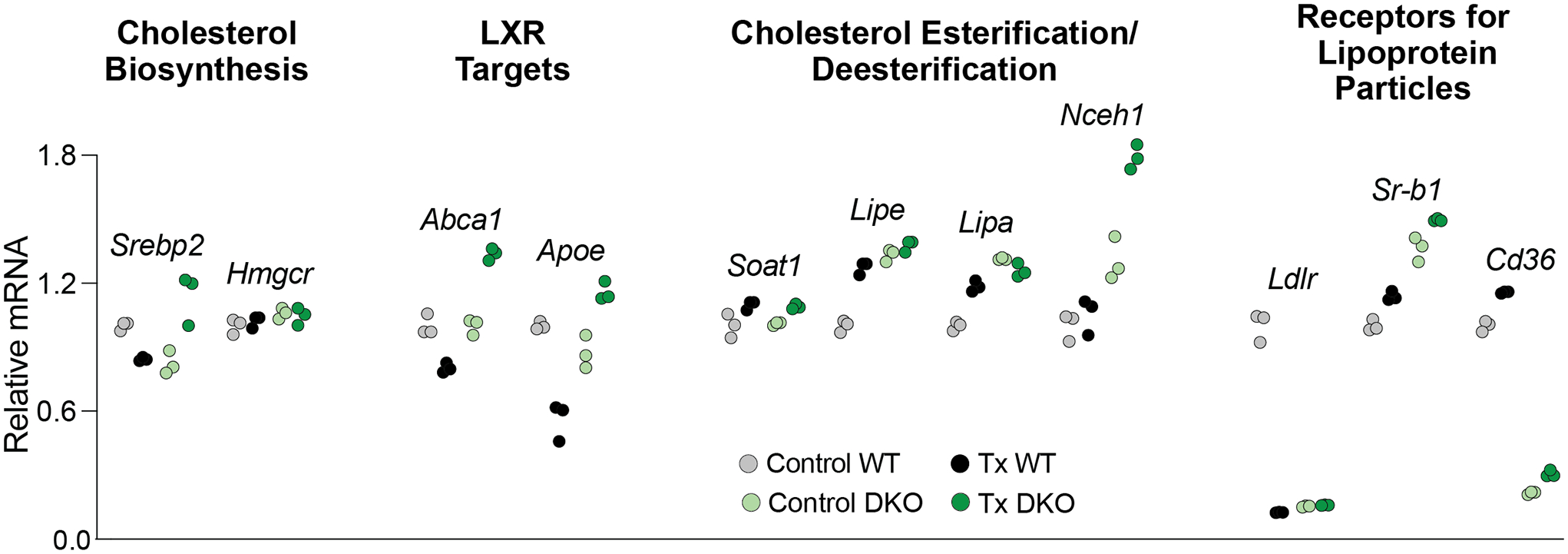
HPCD treatment by oral gavage: effects on retinal gene expression. The treatment paradigm was the same as in Figure 3. Changes in the relative mRNA levels were normalized to the gene expression in control WT mice. Srebp2 encodes a transcription factor, which senses the intracellular cholesterol levels and modulates the expression of many genes involved in the pathway of cholesterol biosynthesis. Hmgcr is one of SREBP2 targets and is the rate limiting enzyme of this pathway. Abca1 encodes a transporter, which effluxes cholesterol excess out of cells. Apoe encodes an apolipoprotein and a constituent of apolipoprotein particles, which accept cholesterol excess effluxed by ABCA1. Soat1 encodes a ubiquitous cholesterol esterifying enzyme, whereas Lipe, Lipa, and Nceh1 are the genes for three different cholesterol ester hydrolyzing enzymes. Ldlr, Sr-b1, and Cd36 encode the plasma receptors for different lipoprotein particles. Dots represent triplicate measurements on one pooled sample of 8 retinas from 8 male mice. Statistical significance was not assessed as n=1. Instead, an arbitrary cut off was used, which was ≥32% change in gene expression between control WT vs control Cyp27a1−/−Cyp46a1−/− mice or between HPCD-treated vs control mice of the same genotype. This cut off represented two times 16%, the highest SD value in our triplicate technical replicates. Cntr, control mice; DKO, Cyp27a1−/−Cyp46a1−/− mice; Tx, HPCD-treated mice; WT, wild type mice.
