Figure 6.
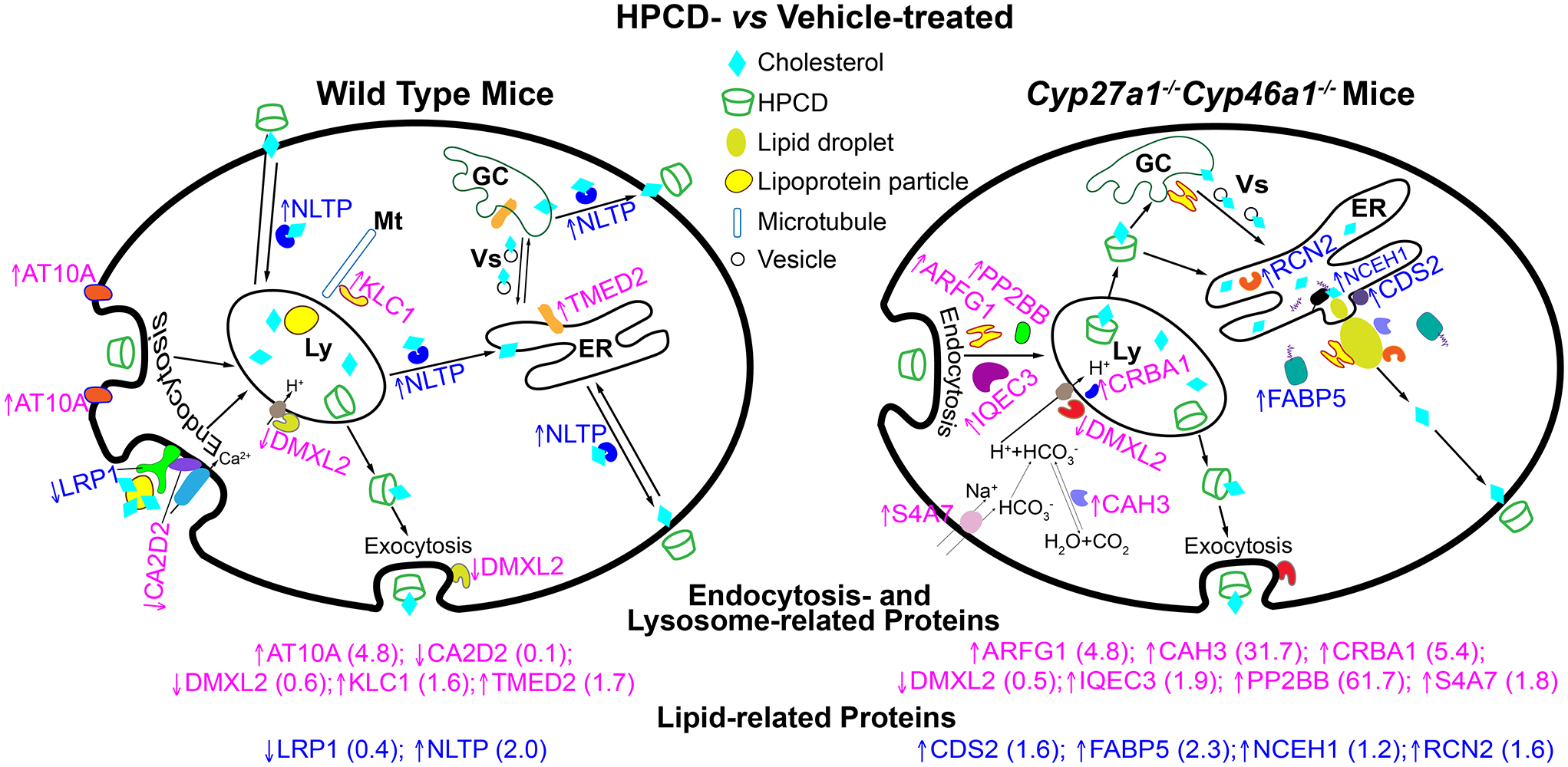
HPCD treatment by oral gavage: effects on retinal proteomics. The treatment paradigm was the same as in Figure 3. Upwards and downwards arrows indicate increased and decreased protein abundance, respectively; a fold-change in abundance is shown in parenthesis. The affected proteins in the WT retina include AT10A, the catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex, which promotes inward bending of the plasma membranes and hence endocytosis (Takada et al., 2018). LRP1 is the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1, which binds and internalizes lipoproteins particles containing cholesterol (Actis Dato & Chiabrando, 2018). LRP1 interacts with CA2D2, the α2δ subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channels, and through this interaction affects the channel function and trafficking (Kadurin et al., 2017). DMXL2 is the α subunit of rabconnectin-3, a multifunction protein, which is involved in the regulation of Ca2+-dependent exocytosis (Kawabe et al., 2003; Nagano et al., 2002). In addition, DMXL2 is required for the V-ATPase-driven lysosomal (Ly) acidification (Merkulova et al., 2015). KLC1 is a light chain of kinesin-1, a microtubule (Mt) motor protein involved in the movement of multiple cytoplasmic organelles, including lysosomes (Pu et al., 2016; Wozniak & Allan, 2006). TMED2 is a transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 2 involved in vesicular (Vs) trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi complex (GC) (Jerome-Majewska et al., 2010). NLTP is a sterol carrier protein-2 important for the intracellular cholesterol and other lipid trafficking (Gallegos et al., 2001; Kraemer et al., 1995; Schroeder et al., 2007). The affected proteins in the Cyp27a1−/−Cyp46a1−/− retina include ARFG1, a multifunctional GTPase-activating protein for ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), which participates in the adaptor protein 2-regulated endocytosis, vesicular biogenesis in the GC (a component of the coat protein I complex), and lipid droplet (LD) formation by transiently associating with LDs (Bai et al., 2011; Gannon et al., 2014; Shiba et al., 2011). IQEC3 is another protein pertinent to ARF1 as IQEC3 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ARF1 (Hattori et al., 2007). PP2BB is a catalytic subunit of the Ca2+-dependent, calmodulin-stimulated phosphatase 2B (calcineurin), a multifunctional enzyme whose activity is required for synaptic vesicle endocytosis (Clayton & Cousin, 2009; Kilka et al., 2009). CRBA1 is a βA3/A1-crystallin, localized in the lysosomes of the retinal pigment epithelium where it regulates endolysosomal acidification by maintaining the activity of the lysosomal V-ATPase complex (Valapala et al., 2016). The V-ATPase-driven lysosomal acidification also requires DMXL2 (see above) (Merkulova et al., 2015). S4A7 is an electroneutral sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 3, which regulates intracellular pH and is essential for phagosome acidification (Bok et al., 2003; Sedlyarov et al., 2018). Intracellular pH is also affected by the activity of CAH3, the carbonic anhydrase 3 that catalyzes reversible hydration of carbon dioxide (Harju et al., 2013). CAH3 was also found on the surface of LDs as is RCN2, a Ca2+-binding, mostly a luminal protein of the endoplasmic reticulum (Ding et al., 2012; Tachikui et al., 1997). CDS2 is a phosphatidic acid cytidylyltransferase 2 and an ER enzyme important for phospholipid metabolism (Inglis-Broadgate et al., 2005). CDS2 was also found to negatively regulate the growth of LDs (Qi et al., 2016). FABP5 is a cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding protein involved in intracellular transport of free fatty acids and thereby cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism (Wu et al., 2010). Finally, NCEH1 is a neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase (also known as KIAA1363 or arylacetamide deacetylase-like 1) tethered to the ER membrane by its N- terminus with its catalytic domain residing in the ER lumen (Igarashi et al., 2010; Okazaki et al., 2008).
