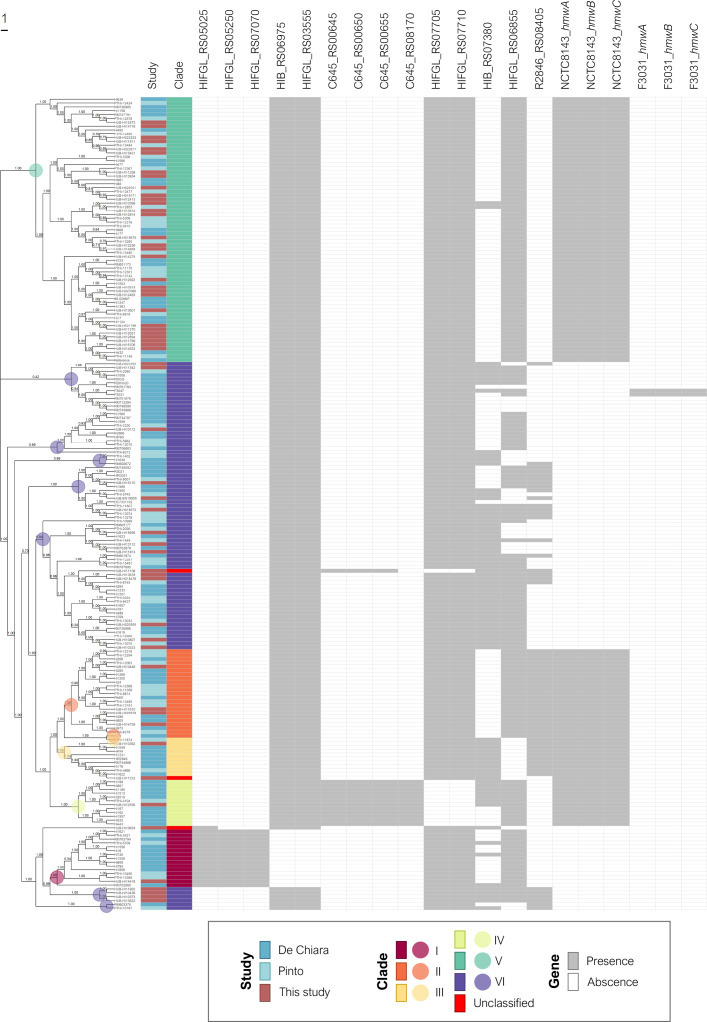
Fig. 4.
Assembly-based core-SNP phylogenetic tree and clade distribution of nontypeable H. influenzae . The tree includes 213 NTHi genomes from three studies: De Chiara et al. [12], Pinto et al. [14] and Carrera-Salinas et al. (this study). Genomes were distributed in different clades (I–VI), as previously proposed according to the presence or absence of 17 accessory genes [12, 14]: HIFGL_RS05025: dinB (DNA polymerase IV); HIFGL_RS05250: ‘YbhB/YbcL family Raf kinase inhibitor-like protein’; HIFGL_RS07070: ‘ABC transporter substrate-binding protein’; HIB_RS06975: ‘7-carboxy-7-deazaguanine synthase QueE’; HIFGL_RS03555: ‘DEAD/DEAH box helicase family protein’; C645_RS00645: ‘Hypothetical protein’; C645_RS00650: ‘pirin family protein’; C645_RS00655: ‘DUF1016 family protein’; C645_RS08170: ‘Hypothetical protein’; HIFGL_RS07705: ‘nucleotidyltransferase domain-containing protein’; HIFGL_RS07710: ‘nucleotidyltransferase substrate-binding subunit’; HIB_RS07380: ‘ABC transporter ATP-binding protein’; HIFGL_RS06855: ‘5-oxoprolinase/urea amidolyase family protein’; R2846_RS08405: ‘TonB-dependent receptor’; NCTC8143_hmwA/B/C and F3031_hmwA/B/C: hmwA/B/C (high molecular weight protein A, B or C). The coloured dots show the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) found in each clade. Relative bootstrap values are given at branch nodes (values below 0.75 are poorly supported).