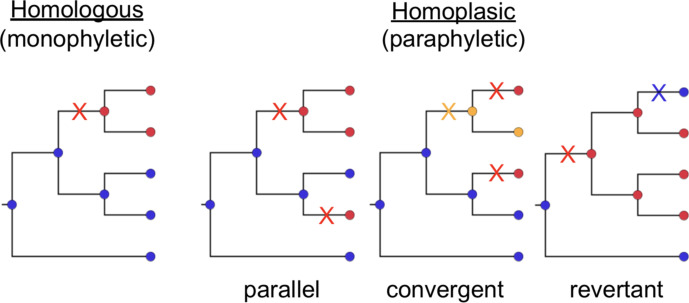
Fig. 1.
Example trees demonstrating the relationship between homology (monophyly) and homoplasy (paraphyly). Homoplasic SNPs can be the result of parallel, convergent or revertant mutation events. Different colours of nodes indicate different nucleotide bases [e.g. blue, adenine (A); red, thymine (T); yellow; guanine (G)]. Different coloured crosses indicate mutations giving rise to the SNPs.