Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Genes with strong positive statistical co-dependency with PPIL4 expression are enriched in brain arterial endothelial cells and Wnt signaling pathway.
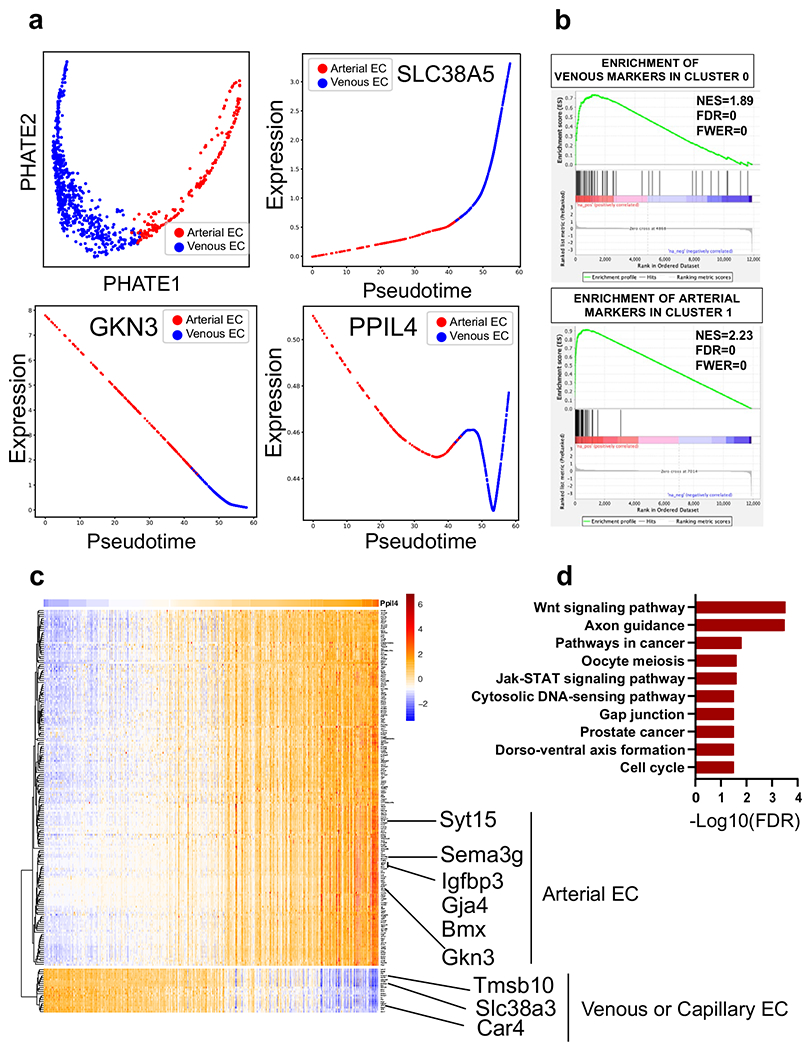
Analysis of publicly available scRNAseq mouse brain endothelial cell datasets obtained from Vanlandewijck et al. & He, L. et al. (PMID: 29443965). a, PHATE plot identifies two major groups in brain endothelial cells, arterial and venous (top left panel). Pseudotime analysis demonstrating PPIL4 expression predominantly in arterial endothelial cells when compared to venous (SLC38A5) and arterial (GKN3) markers. b, GSEA revealing that the top 50 genes associated with venous endothelial cells are significantly enriched among the top ranked genes specifically expressed in Cluster 0. Similarly, GSEA showing significant enrichment of the top 50 arterial endothelial genes among the top ranked genes in Cluster 1. c, Expression of 200 genes with top knn-DREMI score (y axis) ordered by DREVI-based clustering and by peak expression along PPIL4 (x axis). d, Bar plots showing significantly enriched KEGG pathways for genes above 95th percentile knn-DREMI score and positive relationship with PPIL4.
