| IoT |
[96], 2018 |
Crowd Evacuation |
CLOTHO (APA and APA-RF) |
None |
No |
Chemical plant in Nanjing, China |
|
[103], 2018 |
CIoT |
UAVs |
None |
No |
Snow Avalanches |
| Android based |
[104], 2012 |
Evacuation program |
OpenStreetMap |
DMS |
No |
Bangladesh, India |
|
[105], 2014 |
Rescue team tracking |
Algorithm based on location |
GPS-Receiver |
No |
Indonesia |
|
[106], 2016 |
Finding a safezone route |
OpenStreetMap |
PostGIS database |
No |
Makati, Phillipines (Earthquakes) |
| UAV |
[107], 2019 |
Priority based route selection |
Clustering (Bird flocking) |
FANETS |
No |
None |
|
[72], 2019 |
Graph theory, Euler cycle and integer programming |
None |
No |
Hospital Pavia Arecibo |
| ML |
[108], 2015 |
Activating Contraflows |
Decision trees |
Weka (Data mining software) |
Yes |
Hurricanes |
|
[102], 2013 |
Prevent crowd disasters |
SVM, Linear regression and Gaussian model |
GPS Sensors |
Yes |
San Francisco |
|
[81], 2016 |
Determine an evacuation route |
BB-SVM, Dijkstra’s algorithm and Depth first search (DFS) |
ERESS |
Yes |
Kansai university |
|
[36], 2019 |
Deep Neural networks |
Raspberry Pi-3 and spectrum analyzer |
Yes |
Ritsumeikan university |
|
[48], 2019 |
K-medoids and Reinforcement learning |
None |
Yes |
Office scenario |
|
[109], 2017 |
LSTM model |
Spatio and temporal features |
Yes |
Kumamoto earthquakes |
|
[110], 2014 |
Naive Bayes |
None |
Yes |
Fire hazard |
|
[19], 2018 |
SVM and Fuzzy logic |
None |
Yes |
Hajj (A Muslim pilgrimage event) |
|
[45], 2018 |
K-means and hierarchial clustering |
Alarms |
Yes |
An office building |
|
[111], 2016 |
Classification of crowd situation |
Deep CNN and Random Forest |
None |
Yes |
UMN, UCSD and Pets2009 |
|
[46], 2019 |
CNN classifier and K-means |
None |
Yes |
Video data |
|
[50], 2018 |
Planning evacuation route |
Reinforcement learning |
None |
Yes |
Hong Kong fire outbreak |
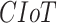 : Cellular IoT,
: Cellular IoT,
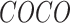 : Common Objects in Context,
: Common Objects in Context,
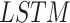 : Long-Short-Term-Memory,
: Long-Short-Term-Memory,
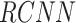 : Recurrent CNN,
: Recurrent CNN,
 : Structural Similarity Index).
: Structural Similarity Index).