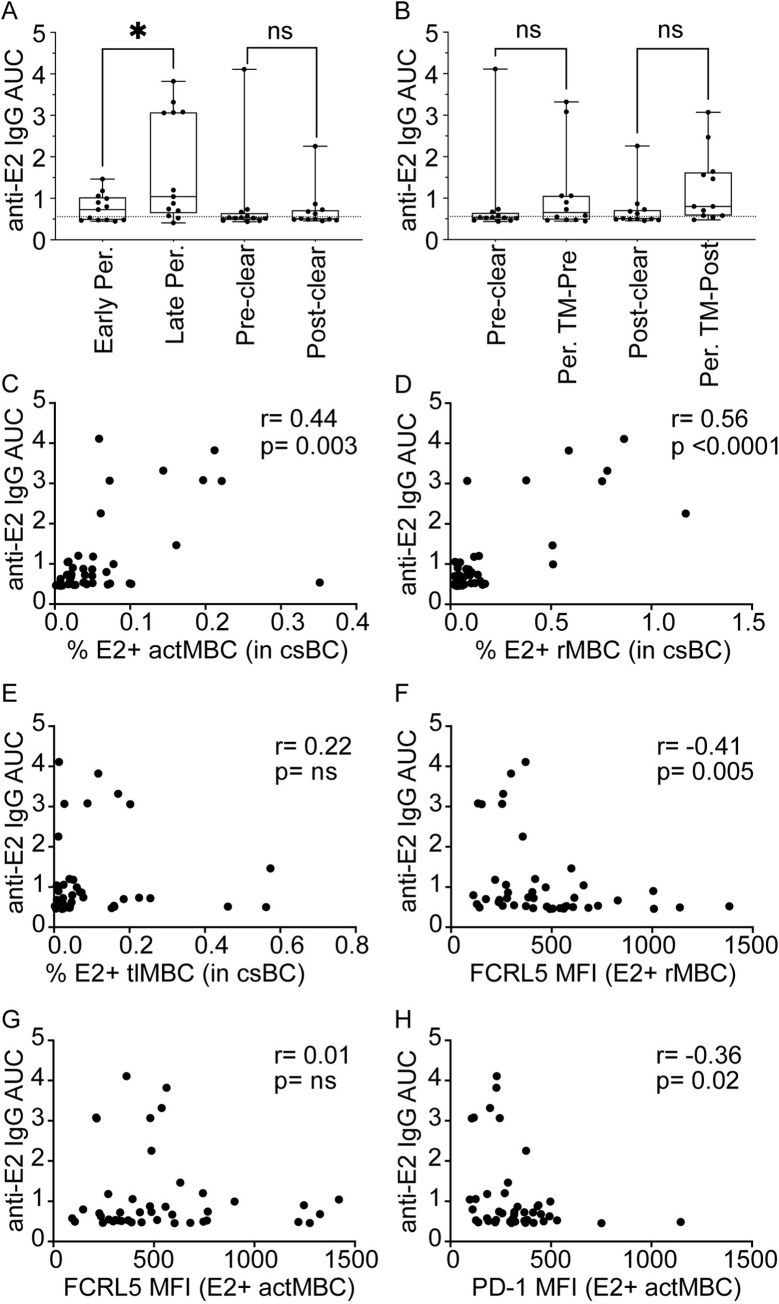
Fig 5. Correlation of plasma anti-E2 IgG levels with E2-specific B cell phenotypes.
(A) Plasma anti-E2 IgG levels of early or late Persistence and pre- or post-Clearance samples determined by calculating area under the curve (AUC). (B) Anti-E2 IgG AUC of Clearance (pre-Clear, post-Clear) or Persistence subjects time-matched with pre- and post-Clearance samples for duration of infection (Per. TM-Pre, Per. TM-Post). (C) Correlation of the frequency (%) of sE2+ resting memory B cells (rMBC) among csBC and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. (D) Correlation of % sE2+ activated MBC (actMBC) among csBC and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. (E) Correlation of % sE2+ tissue-like memory B cells (tlMBC) among csBC and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. (F) Correlation of FCRL5 MFI of sE2+ resting MBC (rMBC) and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. (G) Correlation of FCRL5 MFI of sE2+ actMBC and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. (H) Correlation of PD-1 MFI of sE2+ actMBC and plasma anti-E2 IgG AUC. For A and B, horizontal lines indicate means, boxes are inter-quartile range, and whiskers are minimum to maximum. Two-tailed paired Wilcoxon test (A) or unpaired Mann-Whitney U test (B) for non-normally distributed data was performed with p value adjusted for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni method. * P ≤ 0.05. For C-H, each point indicates a single sample. Early Persistence, late Persistence, pre-Clearance, and post-Clearance samples were included. Correlation r and p values were calculated using the Spearman method.