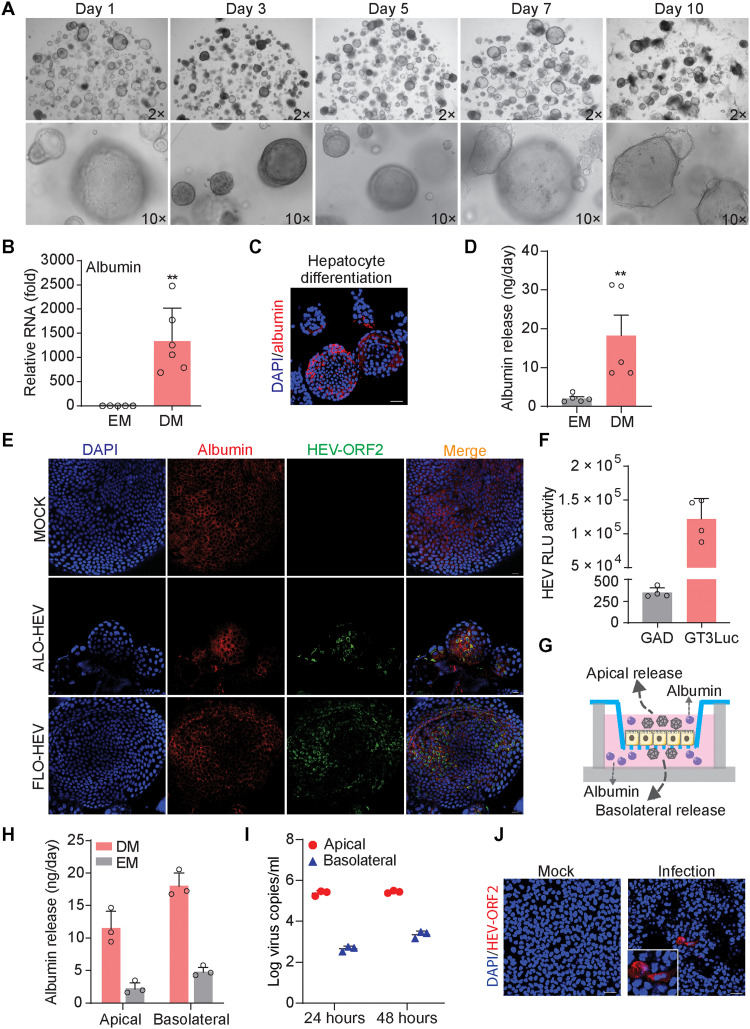
Fig. 5. Hepatocyte-differentiated organoids support HEV replication.
(A) Morphology of hepatocyte-differentiated organoids in different time points. (B) Gene expression level of albumin upon hepatocyte differentiation (n = 5 to 6). EM, expansion medium. (C) Immunofluorescence staining for mature hepatic marker albumin in hepatocyte-differentiated organoids. Scale bar, 40 μM. (D) The secretion of albumin into supernatant quantified by ELISA (n = 5). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of albumin and HEV ORF2 in hepatocyte-differentiated organoids (FLO1 and ALO1 lines were used for differentiation). Scale bar, 20 μM. (F) HEV replication–related luciferase activity in hepatocyte-differentiated organoids (ALO1, n = 4). (G) Illustrating secretion of albumin and HEV from polarized hepatocyte-like cells in a transwell system. (H) Release of albumin into apical and basolateral compartments from polarized cells cultured in EM with cholangiocyte phenotype or DM with hepatocyte phenotype (n = 3). (I) Polarized release of HEV from hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from ICOs harboring p6 HEV genome (ALO1, n = 3). (J) Immunofluorescence staining of HEV ORF2 in Huh7 cells at 48 hours after inoculation of apical released virus from hepatocyte-like cells. Scale bar, 40 μM. Data are presented as means ± SD, **P < 0.01.