Figure 4.
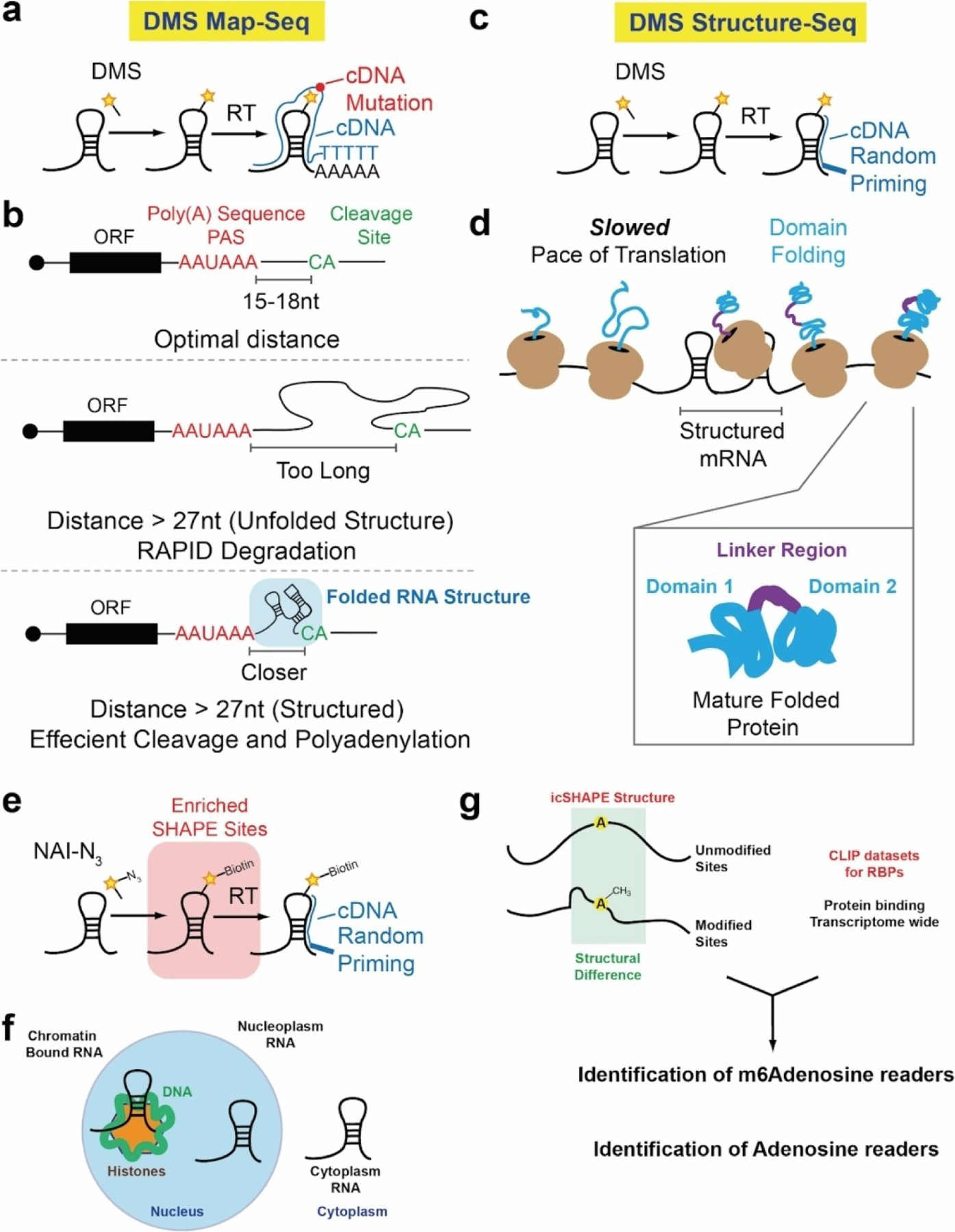
Biological insights gathered from transcriptome-wide analysis of RNA structure. a) DMS MaP-seq schematic. b) DMS MaP-seq reveals that folded RNA structures are responsible for bringing cleavage site (CA) and poly(A) sequences (PAS) into close proximity for efficient cleavage and polyadenylation. c) Schematic of DMS structure-seq. d) DMS structure-seq reveals that mRNA sequences associated with inter-domain regions in proteins have high structural complexity and integrity, which is hypothesized to slow down the rate of translation. This slow down enables the domains to fold correctly. e) Schematic of icSHAPE probing. f) icSHAPE was used to probe RNA structure in different parts of the cell. g) icSHAPE was used in combination with iCLIP datasets. iCLIP datasets profile transcriptome-wide protein occupancy. When used in combination at m6 A sites, icSHAPE was able to identify m6 A readers and adenosine readers specifically, based solely on the structure profile in combination with the CLIP data.
