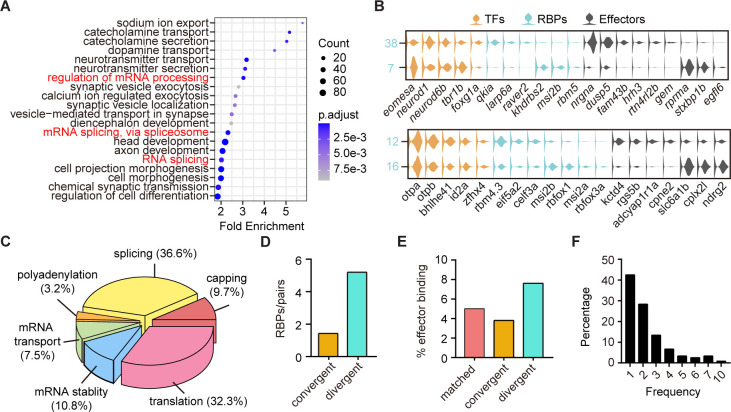
Figure 5. The post-transcriptional regulatory landscape in neurons with different terminal features but similar transcription factor (TF) profiles.
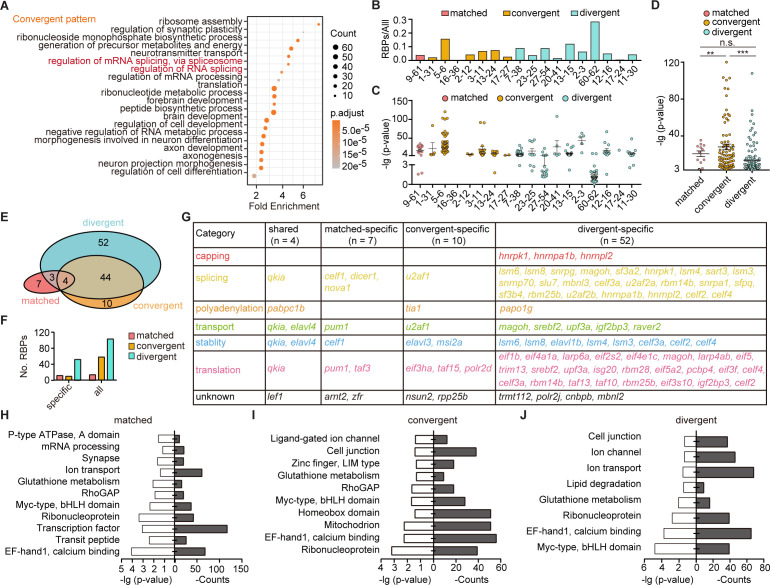
(A) Dot plot showing Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of differentially expressed genes between each pair clusters with divergent pattern. Red highlighted the category of post-transcriptional regulators. The number of genes in each category was coded by dot size, p.adjust of each category was color-coded. (B) Violin plots showing the expression of genes encoding TFs (yellow), RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) (blue), and effector genes (black) in two pairs of neuronal clusters with divergent pattern (7/38 were glutamatergic neurons, 12/16 were GABAergic neurons). (C) 3D pie plot showing the functional annotation of differentially expressed RBP genes identified in A. (D) Bar plot showing the number of pattern-specific RBPs per pair in different patterns. Each pattern was color-coded. (E) Bar plot showing the effector binding target proportion of pattern-specific RBPs. Each pattern was color-coded. (F) Bar plot showing the percentage of one RBP used as differentially expressed genes between pair clusters with different patterns.