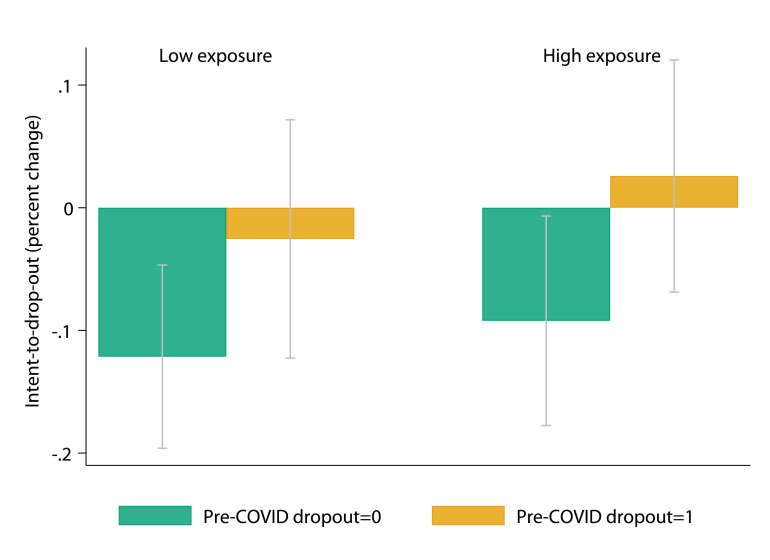
Fig. 4.
Nudge intervention effect heterogeneity by pre-COVID dropout intention and estimated exposure to COVID-related information. Notes: This figure plots the estimated nudge intervention effects and corresponding 95% confidence intervals in gray lines for the four crosstab-ed groups in percentage relative to each subgroup’s control mean. Exposure to COVID index was estimated using a principal component analysis to summarize six main measures: (1) whether a student reported to have paid attention to COVID-19, (2) whether she had a doctor parent, (3) whether faculty members or students in her close social network served on the frontline of COVID-19, (4) whether she had home internet access, (5) whether her college was in Wuhans neighboring provinces, and (6) whether the number of her hometown province had confirmed cases above the national median as of the survey day. Low (High) exposure was defined as having the estimated exposure index smaller (larger) than sample median. The intervention effect was estimated using the same Model 5 in Table 4.