Fig. 3. Example of how VR can be used to create virtual ecologies that measure naturalistic behaviors in participants with chronically implanted electrodes.
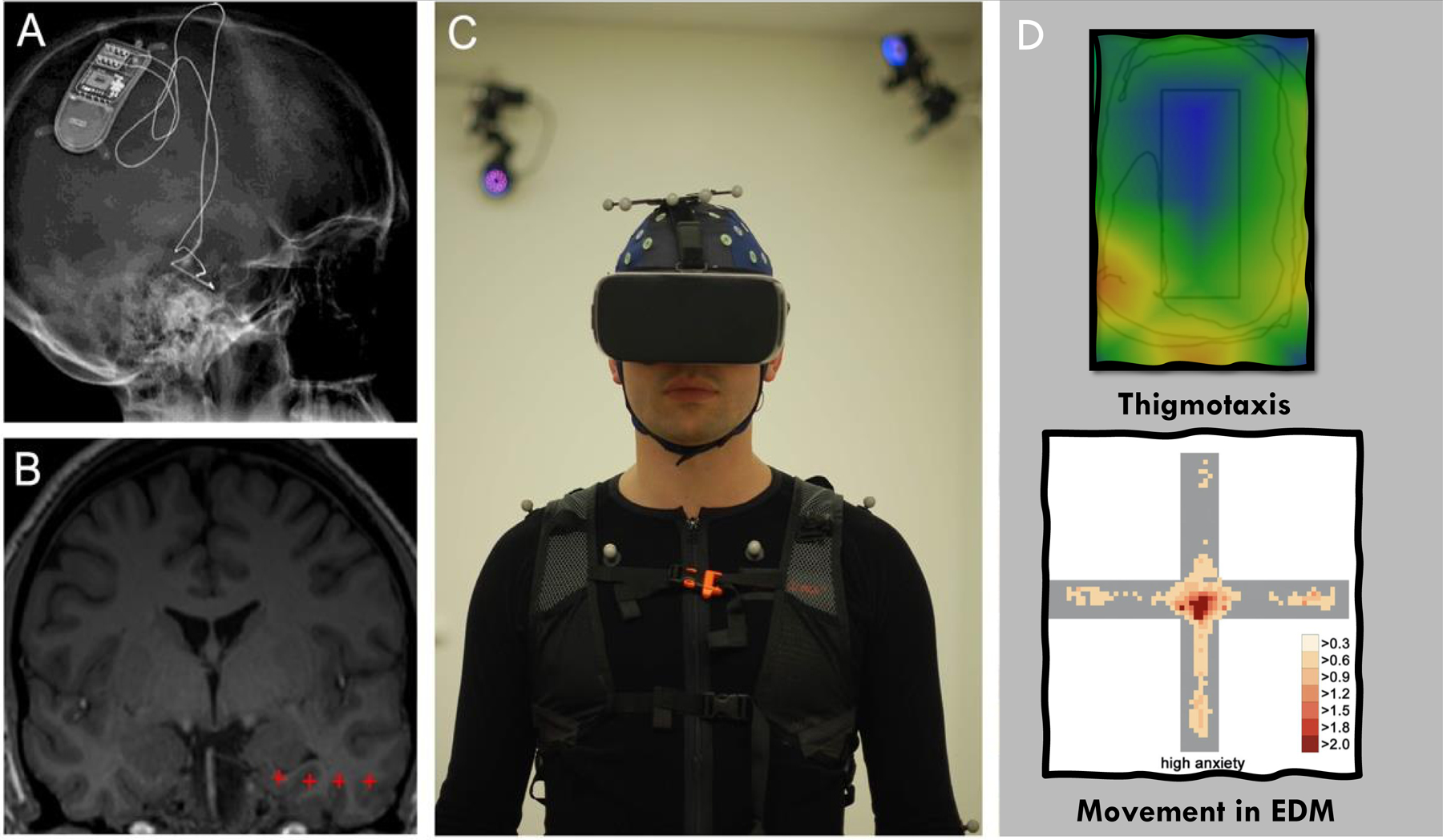
A) X-ray image and B) MRI of an example participant with a chronically implanted electrode with four contacts (red crosses) in the temporal lobe for iEEG recording, during which ambulatory VR and full-body motion capture (C) can be integrated (Stangl et al., 2021). Example of how VR can be used to create virtual ecologies that measure behaviors similar to those observed in rodents (e.g., thigmotaxis ((Walz et al., 2016), and movement in the EDM (Biedermann et al., 2017).
