Figure 2.
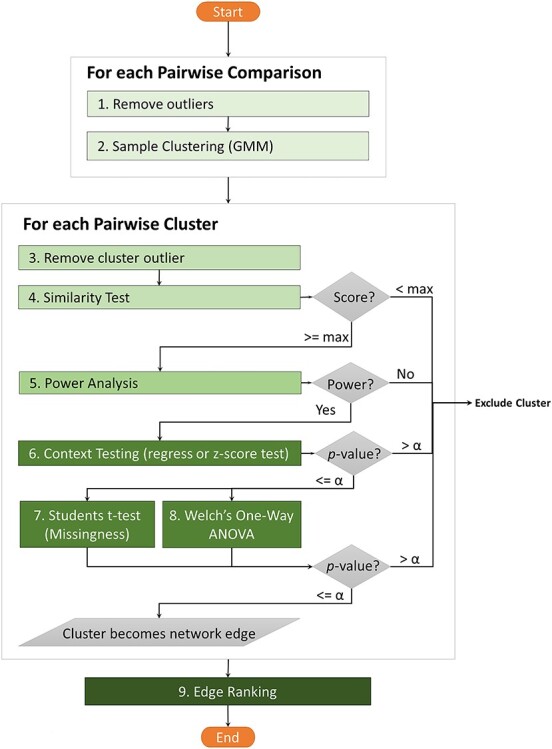
The KINC GCN construction process. The flowchart depicts the eight steps of the KINC workflow for addressing statistical and natural noise in GCN construction. In summary, each pair of genes proceeds through the workflow. First, outliers are removed. Second GMM is performed to identify clusters of expression. Third, cluster outliers are removed and fourth the similarity test (e.g. Pearson or Spearman) is performed. Clusters with a minimum score proceed. Fifth, a power analysis is performed to ensure sufficient statistical power in the correlation test. Clusters with high score proceed. Sixth, clusters are tested for association with context (e.g. experimental conditions) and those with significant P values are associated with the condition and proceed. Seventh, parallel tests for similar patterns of missingness (t-test) and difference in variance (Welch’s one-way ANOVA) are performed. Clusters with significant P values are retained as context-specific edges in the network. Finally, all edges are ranked according to P values and scores to help researcher prioritize edges.
