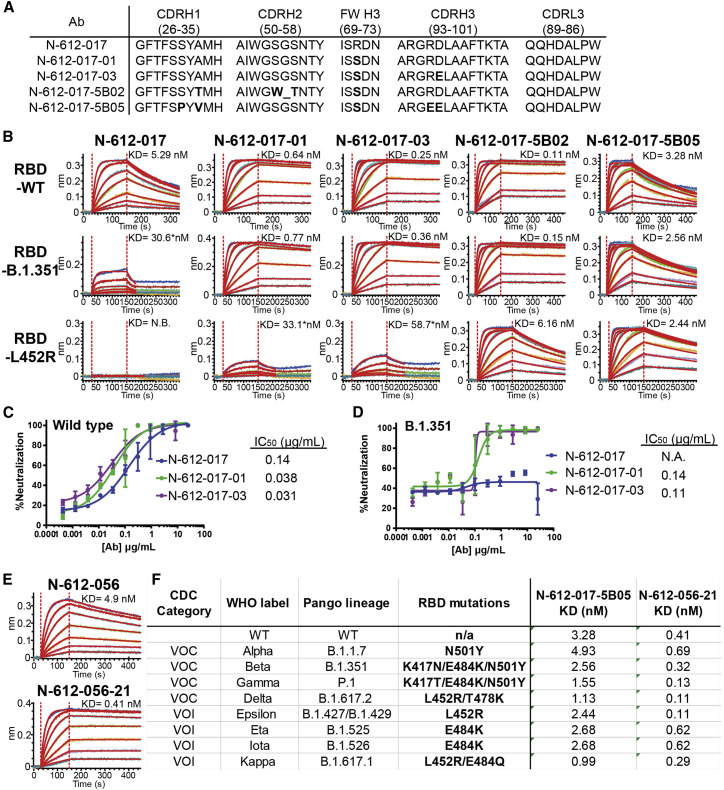
Figure 7.
Affinity maturation of N-612-017 and N-612-056
(A) VH and VL sequences of N-612-017 affinity-matured subclones
(B) BLI kinetic analysis of N-612-017 affinity-matured subclones against RBD-wild type, RBD-B.1.351, and RBD-L452R. Asterisk indicates KD values obtained from processing the data with a shorter dissociation time to fit the curves to a 1:1 binding model and may not represent accurate KD values.
(C and D) SARS-CoV-2 live virus neutralization assay of N-612-017, N-617-017-01, and N-612-017-03 against (C) wild-type and (D) (B)1.351 variants. Mean and standard deviation of duplicate experiments (n = 3) are shown.
(E) BLI kinetic analysis of N-612-056 and affinity-matured N-612-056-21 against RBD-wild type.
(F) Table of binding affinity of N-612-017-5B05 and N-612-056-21 against the RBD containing variant mutations from all the VOCs and VOIs listed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).