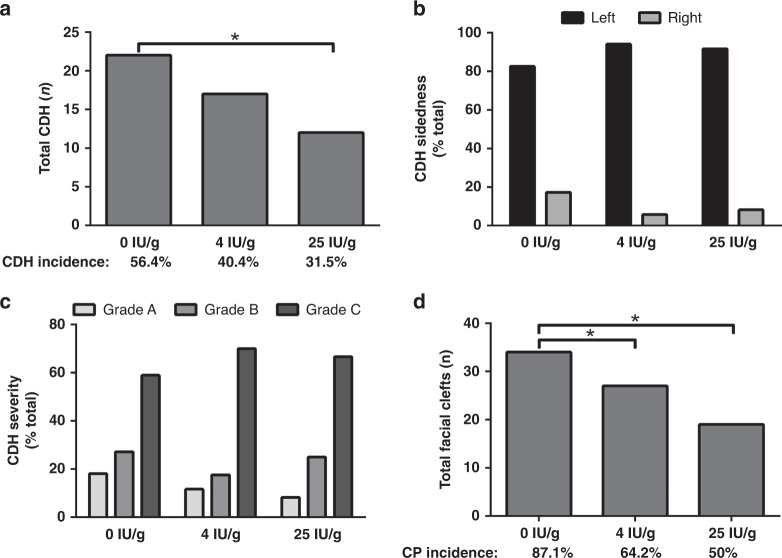
Fig. 3. Altered maternal vitamin A status impacts susceptibility to teratogen-induced CDH.
The total number of diaphragmatic hernia was significantly different between groups with differing vitamin A status (a). Mice consuming a diet with 0 IU/g vitamin A had a significantly higher incidence of CDH than mice consuming a 25 IU/g vitamin A diet. There was no significant difference in the sidedness (b) or severity of diaphragmatic hernia (c). The occurrence of midline facial clefting was significantly different between groups with differing vitamin A status (d). Mice consuming a diet with 0 IU/g vitamin A had a significantly higher incidence of facial clefting than mice consuming 4 or 25 IU/g vitamin A diet. All categorical data analyzed using a X2 test for trend. *p < 0.05, Fishers exact test post-test analysis.