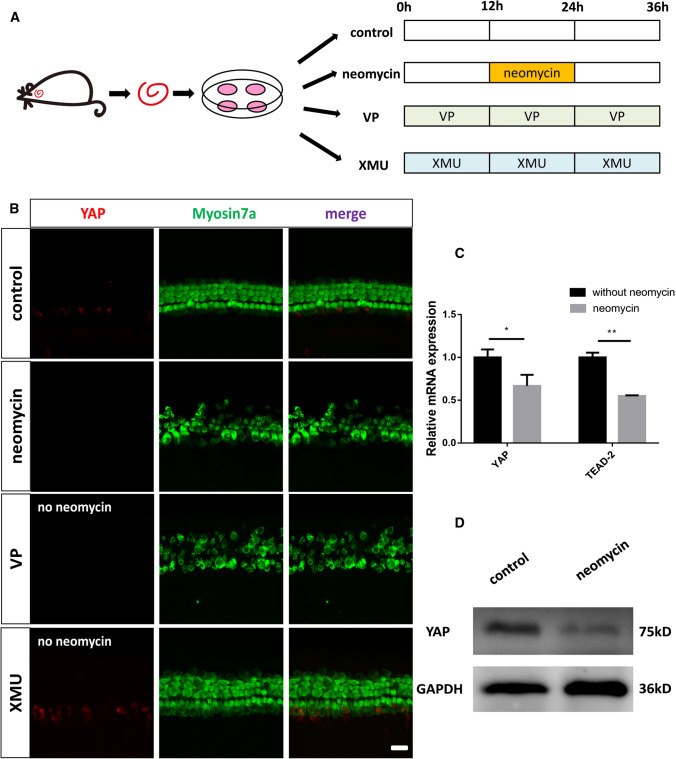
Fig. 2.
The Hippo pathway is activated and the expression of YAP is decreased in cochlear HCs after neomycin treatment. A The dissected cochleae were cultured in vitro with different treatments. In the neomycin-treated group, the cochleae were allowed to recover for the first 12 h, treated with 0.5 mM Neomycin for the next 12 h, and then allowed to recover again for another 12 h. In the VP-treated group, the cochleae were cultured with 5 μM VP for 36 h without neomycin. In the XMU-treated group, the cochleae were cultured with 5 μM XMU for 36 h without neomycin. B Immunofluorescence staining showed that the expression level of YAP was decreased in the HCs after neomycin treatment compared with the control group and that the expression of YAP was upregulated in the XMU-treated group and downregulated in the VP-treated group. The HCs were lost after VP treatment. C qPCR results revealed that the expression of YAP and the Hippo downstream target gene TEAD-2 was significantly downregulated after neomycin treatment. D Western blot results showed that the expression of YAP was decreased in the HCs after neomycin injury. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n = 3. Scale bars = 20 µm