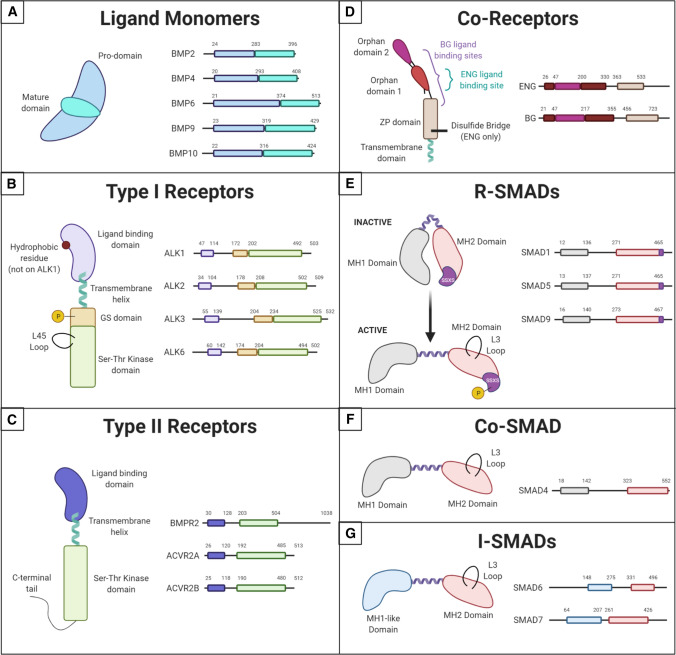
Fig. 2.
Structure of BMP Pathway Components. Comparison of the structures of different components used in endothelial cell BMP signaling, highlighting important functional domains. A BMP ligand monomers have a pro-domain and a mature domain. Ligands often pair to make homodimers, although heterodimers have been reported. B Type I receptors share a ligand-binding domain with a hydrophobic residue on ALK2, 3, and 6, but not ALK1. They are phosphorylated by Type II receptors on their GS domain. Their active site is in the Ser–Thr kinase domain on the C-terminal end of the protein. This domain also contains the L45 loop that binds the R-SMAD L3 loop. C Type II receptors have a similar structure to Type I receptors but lack the GS domain and some contain a long C-terminal tail important for non-canonical signaling. D BMP Co-Receptor endoglin (ENG) dimerizes through a disulfide bridge in its ZP domain and binds ligands in the Orphan Domain 1. Betaglycan (BG) is a monomer that wraps around its ligand with both Orphan Domains and the N-terminal region of its ZP domain. Both co-receptors have short transmembrane domains with no signaling functionality. E–G All SMADs contain an MH2 domain with an L3 loop capable of binding the L45 loop on Type I receptors, connected to an MH1 domain (or MH1-like domain in i-SMADs) by a linker region. R-SMADs maintain an inactive, folded conformation until they are phosphorylated on the SSXS motif within their MH2 domain by Type I receptors