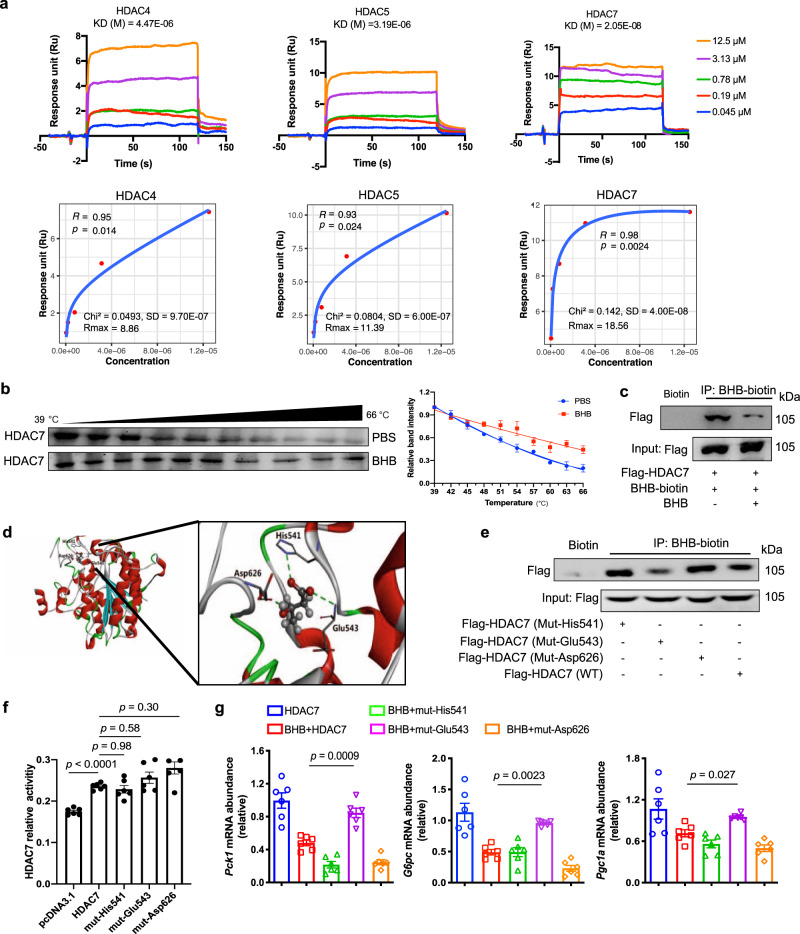
Fig. 6. The potential interaction between BHB and HDAC7.
a The interaction of BHB with HDACs by surface plasmon resonance. A series of BHB concentrations was injected onto the HDAC4, HDAC5 or HDAC7 biosensor surface. The frequency response and fitting curves were displayed. b CETSA for in-cell HDAC7 target engagement. Representative western blots showed thermostable HDAC7 with indicated heat shocks in the presence or absence of BHB (50 µM, n = 3). c Immunoprecipitation analysis of interaction between biotin-BHB and HDAC7 in primary hepatocytes transfected with HDAC7 plasmid with or without unlabeled BHB treatment. It was repeated 3 times independently with similar results. d Binding modes and sites of BHB with HDAC7 predicted by AutoDock. The protein is shown as cartoon and BHB as sticks. e Immunoprecipitation analysis of interaction between BHB-biotin and HDAC7 in HEK-293T cells transfected with HDAC7 (WT, Mut-His541, Mut-Glu543 or Mut-Asp626) plasmid. It was repeated 3 times independently with similar results. f Enzyme activity of HDAC7 in HepG2 cells transfected with HDAC7 (WT, Mut-His541, Mut-Glu543 or Mut-Asp626) plasmid (n = 5). g Relative mRNA abundance of Pck1, G6pc and Pgc1a in primary hepatocytes transfected with HDAC7 (WT, Mut-His541, Mut-Glu543 or Mut-Asp626) plasmid after BHB treatment (n = 6). Asp aspartic acid, BHB β-hydroxybutyrate, CETSA, cellular thermal shift assay, GLC glucagon, Glu glutamic acid, His histidine, Mut mutant, WT wild type. Values represent mean ± SEM. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.