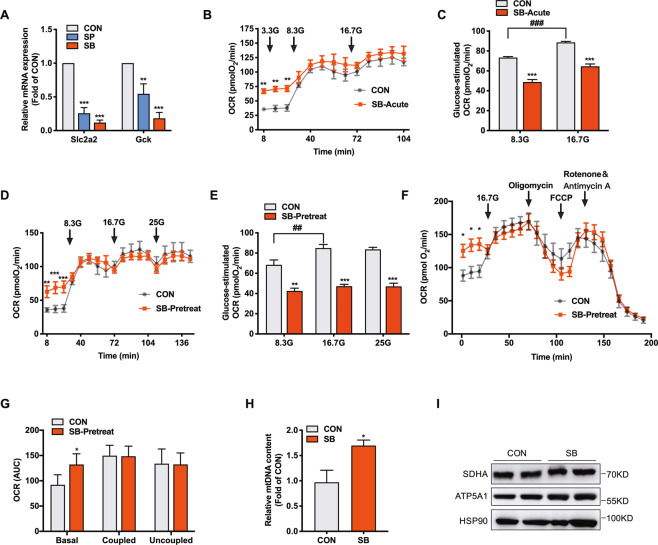
Fig. 5. Sodium butyrate treatment decreases glucose oxidation in rat islets.
A RT-qPCR analysis of Slc2a2 and Gck mRNA expressions in rat islets incubated with 5 mM sodium butyrate (SP) or 5 mM sodium propionate (SB) for 24 h. B Basal and glucose-stimulated oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in rat islets treated with 5 mM SB for 1 h. C Determination of glucose-stimulated OCR based on B. D Basal and glucose-stimulated OCR in rat islets treated with 5 mM SB for 24 h. E Determination of glucose-stimulated OCR based on D. F After rat islets were treated with 5 mM SB for 24 h, OCR was measured in the presence of 25 mM glucose, 1 μM oligomycin, 2 μM FCCP, or 0.5 μM rotenone/antimycin A at the indicated time points (arrows). G Determination of basal, coupled, and uncoupled respiration in F. H mtDNA content in INS-1 cells treated with 5 mM SB for 24 h. I SDHA (Complex II) and ATP5A1 (Complex V) protein expressions in INS-1 cells treated with 5 mM SB for 24 h. Data were given as mean ± SD for three separate experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs control (CON) group. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001.