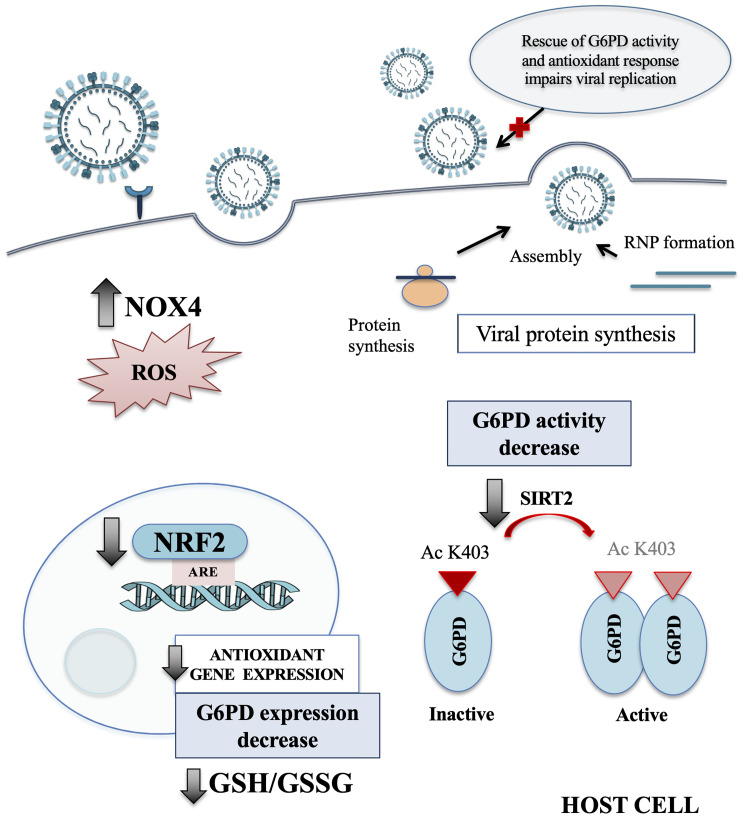
Figure 7.
Influenza virus infection affects the host antioxidant response. Schematic representation of the main redox-related pathways modulated by influenza virus infection. NRF2 protein is present at lower level into the nucleus of host infected cells, leading to a drop of the antioxidant gene expression, including G6PD. The reduction of SIRT2 expression affects the activation of G6PD enzyme that in turn leads to GSH/GSSG ratio decrease. Moreover, the infection induces oxidative stress condition also by increasing the NOX4-mediated ROS production. Finally, we observed that the rescue of NRF2 and G6PD expression impairs influenza virus replication. NOX4, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ARE, antioxidant response elements; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized form of GSH; SIRT2, sirtuin 2; Ac K403, acetylated lysine 403; RNP, ribonucleoprotein.