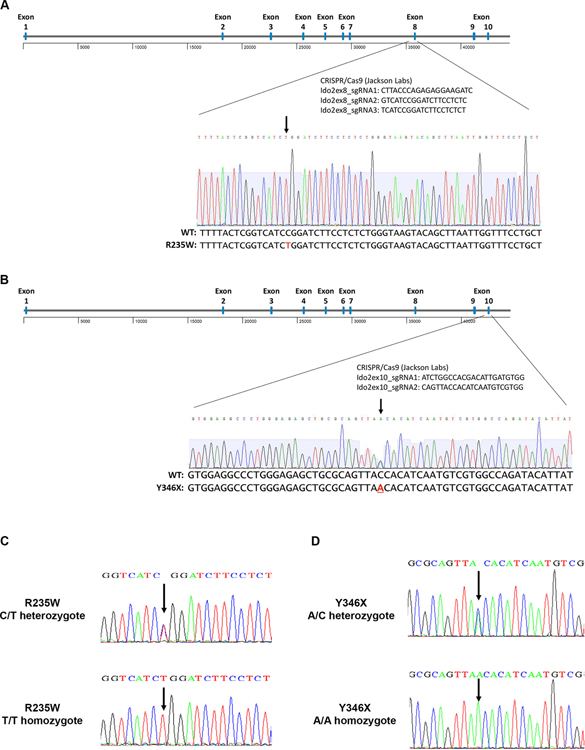
Figure 1. Generation of catalytically inactive IDO2 polymorphism knock-in mice.
Point mutations were introduced into the mouse IDO2 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 to recapitulate the enzyme-inactivating (A) C/T polymorphism at position 235 that introduces an R to W amino acid change in exon 8 and (B) C/A polymorphism at position 346 that introduces a stop codon in exon 10. Sequences for the CRISPR guides are indicated. Successful knock-in of the Ido2 polymorphisms were confirmed for both founder and experimental mice by sequencing of genomic DNA. Representative traces for mice heterozygous and homozygous for (C) R235W and (D) Y346 polymorphisms are shown.