Figure 3. IDO2 enzymatic activity is not required for joint inflammation or autoantibody production in KRN.g7 model of autoimmune arthritis.
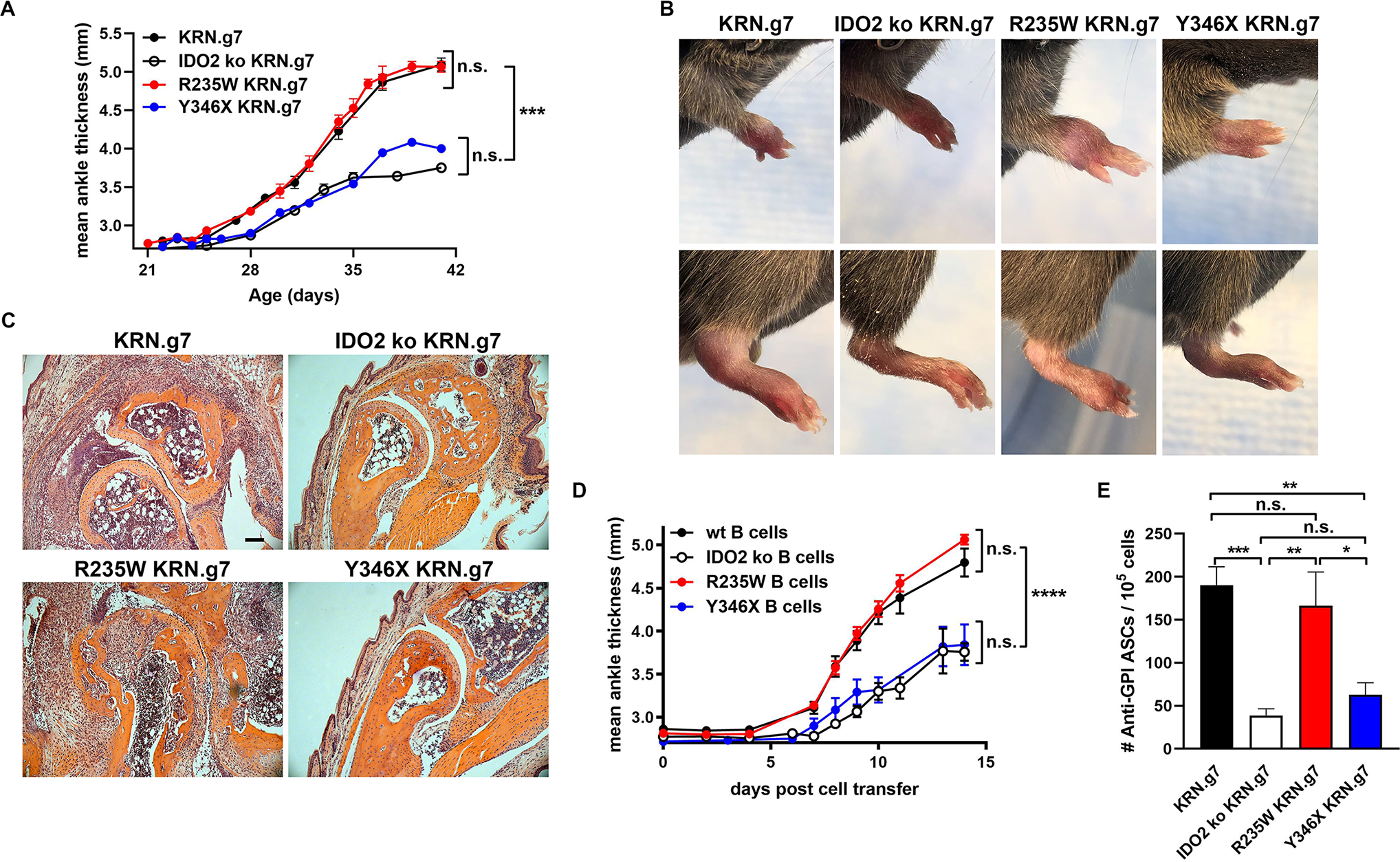
(A) Rear ankles were measured as an indication of arthritis and represented as the mean change in ankle thickness ± SEM from n=12 KRN.g7, n=14 IDO2 ko KRN.g7, n=9 R235W KRN.g7, and n=8 Y346X KRN.g7 mice, pooled from 4 independent litters for each genotype. At 6 wk of age, (B) pictures were taken of the front and rear paws and (C) rear paws were sectioned and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Representative images from a total of n=8 mice per genotype. Scale bar = 100μm. (D) Arthritis was induced by adoptively transferring KRN IDO2 ko T cells into IDO2 ko TCRα ko B6g7/b mice together with B cells purified from B6g7/b (wt), IDO2 ko B6g7/b (IDO2 ko), R235W B6g7/b (R235W), or Y346X B6g7/b (Y346X) mice. Arthritis is represented as mean ankle thickness ± SEM. Data is from n=7 wt, n=7 IDO2 ko, n=14 R235W, and n=5 Y346X B cell transfers. (E) The number of anti-GPI ASCs from the joint dLNs was determined using an ELISpot assay. Data shows the mean number of ASCs ± SEM for n=29 KRN.g7, n=14 IDO2 ko KRN.g7, n=14 R235W KRN.g7, and n=14 Y346X KRN.g7 mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, n.s., not significant.
