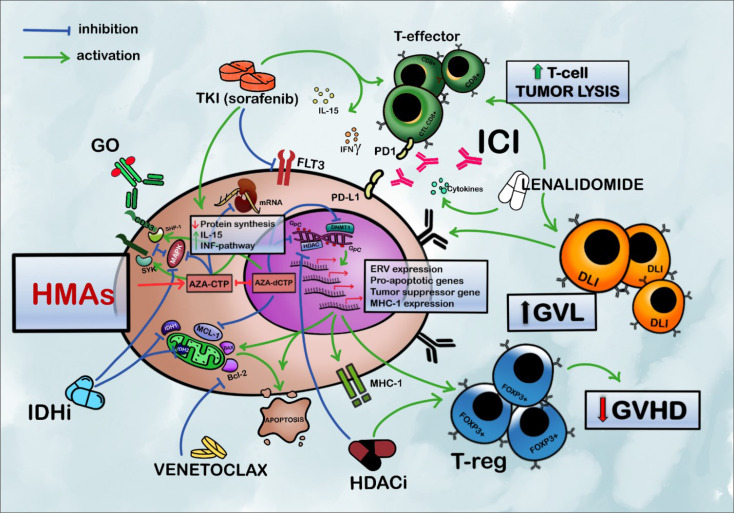
Figure 1.
Rationale for HMA-based combination strategies in acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic HSCT. HMAs sensitize blasts to the T cell-mediated immune response by upregulation of IFN-pathway genes, increased expression of MHC-1, and ERV. The expansion of FOXP3 + T regs mediated by HMAs facilitates GVL preserving from GVHD. HMAs also upregulate antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells (not pictured). Promoting the modulatory activity of Tregs, AZA greatly reduces the risk of severe GVHD and emphasizes GVL; BCL-2 inhibitors restore mitochondrial apoptotic pathways and sensitize AML cells to HMAs. AZA may, also, synergize to activate BAX pro-apoptotic gene and reduce levels of MCL-1. Sorafenib inhibits FLT3-ITD and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. It also increases cell-mediated immune response enhancing IL-15 production and INFγ-pathway synergizing with allogeneic effective T cells. Lenalidomide increases the activity of T-effectors and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines; HMAs can reverse the hypermethylation of DNA induced by IDH-mutated clones and synergize with the inhibitory activity of IDHi. HMAs and IDHi, also, synergistically inhibit MAPK/ERK signaling; HDAC inhibitors, especially panobinostat, contribute to the epigenetic modulation and can reinduce the expression of TNF receptors on T-regs favoring control over GVHD and an increase in GVL activity. HMAs increase the expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 representing a possible mechanism of resistance to HMAs. PD-1 inhibition can enhance response to DLI and allogeneic effective T cell and consequent T cell-mediated tumor lysis. HMAs increase CD33 expression with consequently increased uptake of GO by AML cells. It also increases the expression of Syk and SHP1, which contribute to GO-mediated cytotoxicity by inhibiting cell growth. HMAs (mostly AZA) decrease P-glycoprotein expression, which contributes to GO resistance (not pictured). HMAs, hypomethylating agents; IDHi, isocitrate dehydrogenase inhibitors; HDACi, histone deacetylase inhibitors; GO, gemtuzumab ozogamicin; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitors; AZA-CTP, azacytidine-cytosine triphosphate; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitors; DLI, donor lymphocyte infusion; GVL, graft versus leukemia; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; AZA-dCTP, azacytidine-deoxy cytosine triphosphate; GpC, GpC island; DNMT1, DNA-methyl-transferase 1; HDAC, histone deacetylase; SYK, spleen-associated tyrosine kinase; SHP-1, Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; BCL-2, B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; FLT3, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3; MCL-1, myeloid cell leukemia-1; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; T-regs, regulatory T cells; ERV, endogenous retrovirus; MHC-1, major histocompatibility complex, class I.