Figure 3.
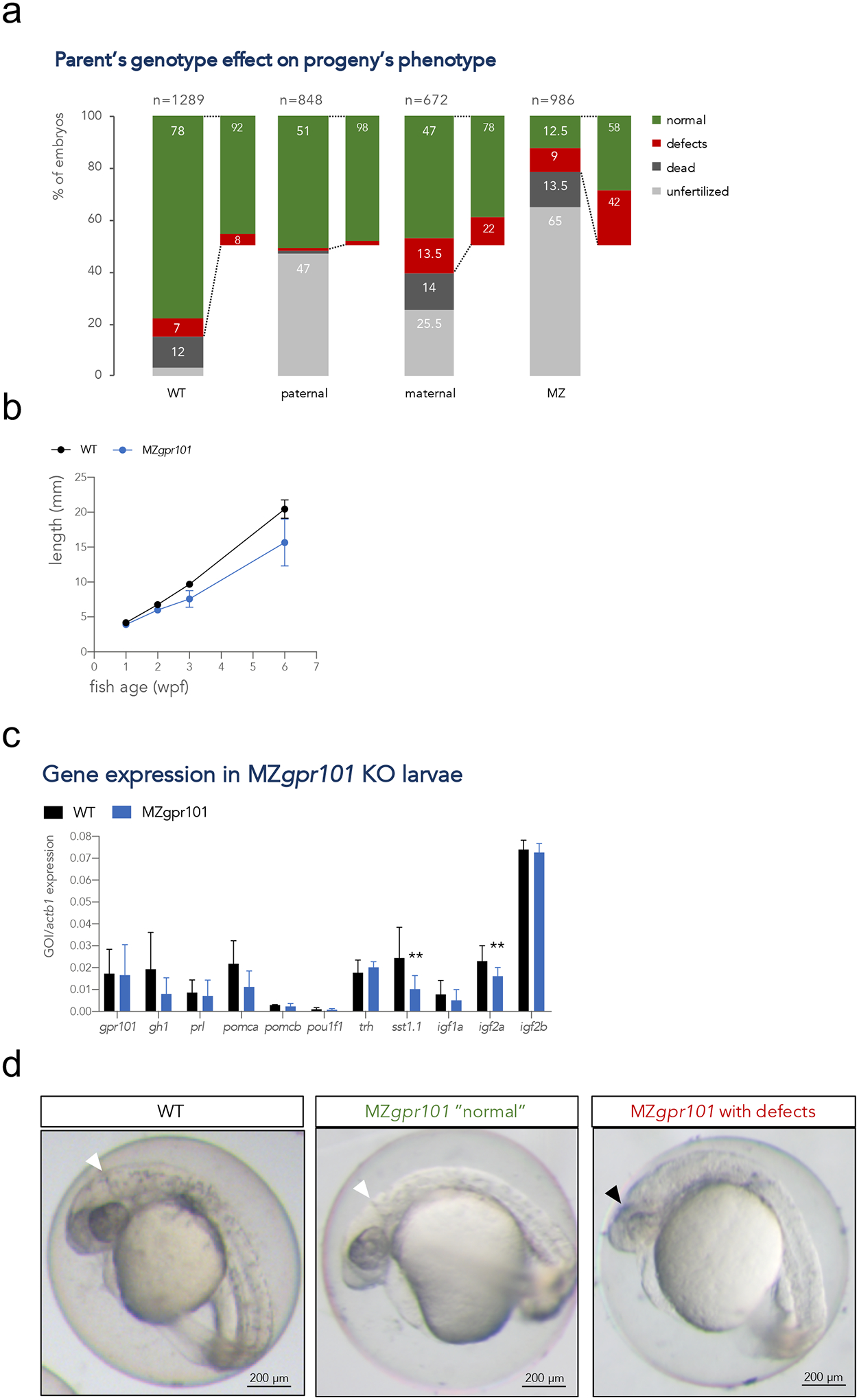
a) Embryos from parents of four different genotypic combinations were generated to assess the parent-of-origin’s contribution to phenotypes: WT (gpr101+/+ embryos from 4 crosses), paternal mutants (gpr101+/− embryos from 4 crosses, which have the maternal and zygotic gpr101, but lack potential paternal gpr101), maternal mutants (gpr101+/− embryos from 1 harem cross consisting of two females and two males, which lack maternal, but contain zygotic and potential paternal gpr101), maternal-zygotic (MZ, gpr101−/− embryos from five crosses, which lack maternal, zygotic and potential paternal gpr101). Each column indicates the percentage of phenotypes observed at morphological inspection at 1 dpf. The total number of analyzed embryos is shown at the top of each column. For the WT controls crosses, 485 fertilized embryos out of 1289 eggs were assessed; for the maternal cross, 128 fertilized embryos out of 672 eggs were assessed. b) Growth measurements for single-housed WT (black) and MZgpr101 mutants (blue). Standard length was measured at 1, 2, 3, and 6 wpf. The number of fish for each genotype at all time points is given in Supplementary Figure 8a. Data were analyzed by a two-way ANOVA; p < 0.001. c) The mRNA expression of gpr101, pituitary and hypothalamic genes, and growth regulators was measured by RT-qPCR in 1 wpf larvae. actb1 was used as endogenous control. GOI: gene of interest. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. d) Representative MZgpr101 embryos showing a WT-looking (normal) embryo (left panel) and an embryo lacking the midbrain-hindbrain boundary and showing brain necrosis (right panel). Seven out of 61 fertilized embryos (11.5%) presented with midbrain-hindbrain boundary defects and necrotic areas in the brain. The white arrowhead indicates the midbrain-hindbrain boundary, while the black arrowhead indicates a necrotic area. Anterior is right. Scale bar: 200 μm.
