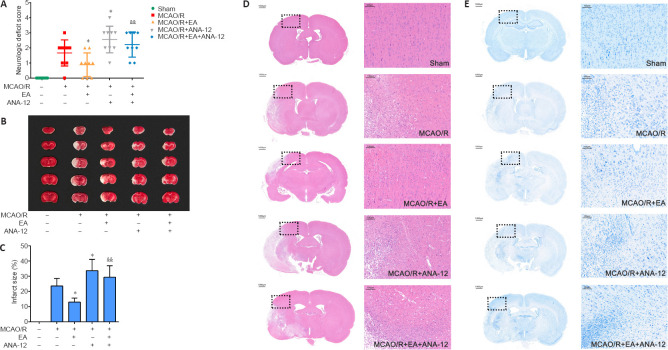
Figure 3.
Effects of EA on MCAO/R-induced brain injury in rats at 7 days after MCAO/R.
EA was applied at the LI11 and ST36 acupoints in MCAO/R-treated rats. ANA-12 was delivered via intraperitoneal injection at 0.5 mg/kg once per day for 7 consecutive days. (A) Effect of EA on neurological deficit scores 7 days after MCAO/R according to the Zea Longa score (n = 9). (B) 2,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining of brain slices. Normal tissue is shown in red and infarcted tissue in white. The infarct volume in the MCAO/R group was significantly increased compared with that in the sham group, the area of the cerebral infarction was significantly decreased after EA compared with that in the MCAO/R group, and ANA-12 attenuated the effect of EA treatments. (C) Quantitative analyses of infarct size (n = 6). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, vs. sham group; *P < 0.05, vs. MCAO/R group; &&P < 0.01, vs. MCAO/R + EA group (one-way analysis of variance followed by least significant difference post hoc test). (D, E) Representative hematoxylin-eosin and Nissl staining performed on sections from ischemic brains (n = 6). The ischemic penumbra histopathological alterations and neuronal loss induced by the MCAO/R were alleviated after treatment with EA. Scale bar: 1000 μm (left) and 100 μm (right). The experiments were repeated three times. ANA-12: TrkB inhibitor; EA: electroacupuncture; MCAO/R: middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion; TrkB: tyrosine kinase B.