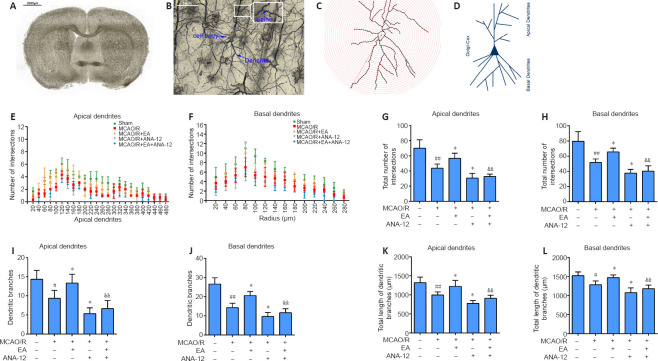
Figure 6.
EA promotes dendritic branching and growth in the ischemic penumbra.
EA treatment was performed at the LI11 and ST36 acupoints in MCAO/R rats. ANA-12 was delivered via intraperitoneal injection at 0.5 mg/kg once per day for 7 consecutive days. (A–C) A representative coronal Golgi-Cox staining section illustrating the phenomenon of MCAO/R injury. Scale bars: 2000 μm in A and 50 μm in B. (D) Illustration of the demarcation between the apical and basal dendrites. (E, F) Sholl analysis of the complexity of the dendritic arborization of neurons, represented as dendritic intersections at a given distance from the soma. (G, H) Total number of apical (G) and basal (H) intersections. (I, J) Number of apical (I) and basal (J) dendritic branches. (K, L) Quantification of total apical (K) and basal (L) dendritic length. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, vs. sham group; *P < 0.05, vs. MCAO/R group; &&P < 0.01, vs. MCAO/R + EA group (one-way analysis of variance followed by least significant difference post hoc test). The experiments were repeated three times. ANA-12: TrkB inhibitor; EA: electroacupuncture; MCAO/R: middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion; TrkB: tyrosine kinase B.