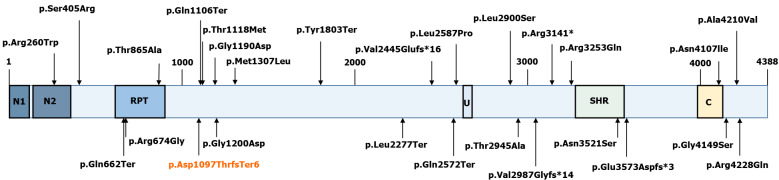
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the VPS13D protein (RefSeq NM_015378). The novel p.Asp1097ThrfsTer6 mutation is marked red. The others are mutations that have since been found in other studies: p.Ser405Arg, p.Thr1118Met, p.Arg3141*, and p.Thr2945Ala (Koh et al[13], 2020); p.Gly1190Asp, p.Ala4210Val, p.Met1307Leu, p.Gly4149Ser, p.Asn4107Ile, p.Gln1106Ter, p.Tyr1803Ter, p.Gln662Ter, p.Gln2572Ter, p.Val2987Glyfs*14, and p.Leu2277Ter (Seong et al[7], 2018); p.Val2445Glufs*16, p.Leu2900Ser, p.Asn3521Ser, p.Glu3573Aspfs*3, p.Arg4228Gln, p.Arg3253Gln, p.Leu2900Ser, p.Thr865Ala, p.Arg674Gly, and p.Gly1200Asp (Gauthier et al[12], 2018); p.Arg260Trp (McCarthy et al[14], 2014); p.Arg674Gly (Shamseldin HE et al[16], 2017); and p.Leu2587Pro (Lee JS et al[15], 2020). N1: VPS13 1st N-terminal domain (aa 2-115); N2: VPS13 2nd N-terminal domain (aa 137-356); U: Ubiquitin-associated (UBA)-like domain (aa 2627-2679); SHR: VPS13 SHORT ROOT transcription factor-binding domain (aa 3276-3558); C: VPS13 C-terminal domain (aa 3983-4129).