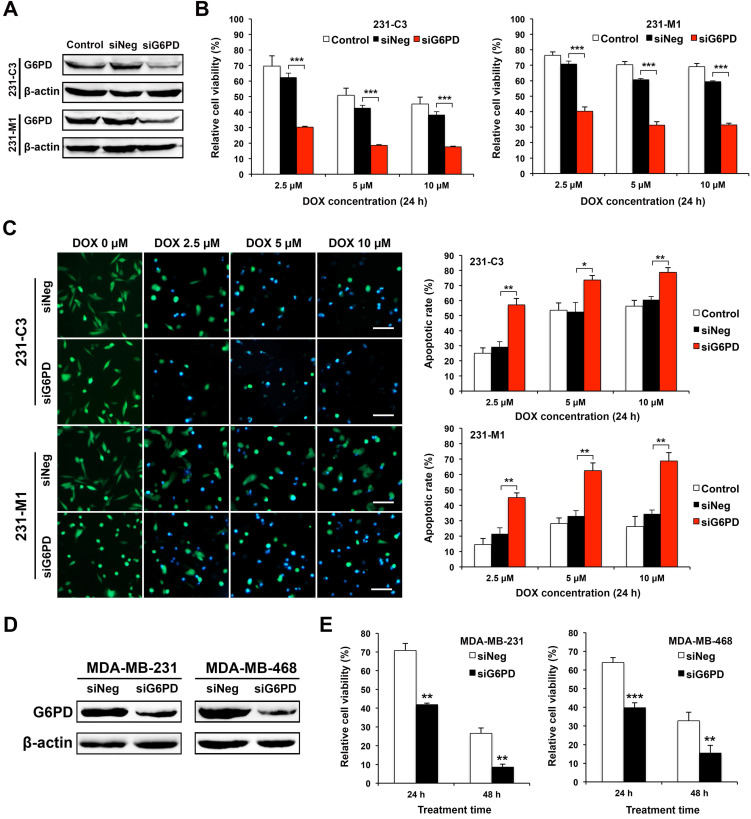
Figure 4.
Downregulating G6PD expression reduces cell viability and increases apoptotic rate of TNBC cells upon DOX treatment. (A) Western blot results of G6PD levels in 231-C3 and 231-M1 cells that were not transfected or transfected with 20 nM of siNeg (siRNA negative control) or siG6PD. (B) G6PD silencing by siRNA decreased cell viability of both 231-C3 and 231-M1 cells upon DOX treatment. After 45 h post siRNA transfection, 231-C3 or 231-M1 cells were treated with DOX at 2.5 µM, 5 µM, and 10 µM respectively for 24 h. The results were normalized to viability of cells without DOX treatment nor siRNA transfection. (C) G6PD silencing by siRNA increased apoptotic rates of both 231-C3 and 231-M1 cells. Left panel shows representative FRET images of 231-C3 and 231-M1 cells with either siNeg or siG6PD treatment that were further subjected to DOX treatment at 0 µM, 2.5 µM, 5 µM, and 10 µM respectively for 24 h. Scale bar, 100 µm. Right panels show apoptotic rates of 231-C3 and 231-M1 cells that were quantified using at least 300 cells from more than five FRET images. (D) Western blot analysis of G6PD levels in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells that were transfected with 20 nM of either siNeg or siG6PD. (E) G6PD silencing by siRNA decreased cell viability of both MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells. After 45 h post siRNA transfection, the cells were treated with DOX at 5 µM for either 24 h or 48 h before subjected to MTT assay. The results were normalized to the control group without DOX treatment.